Figure 1. lag mutation preferentially affects the brain.
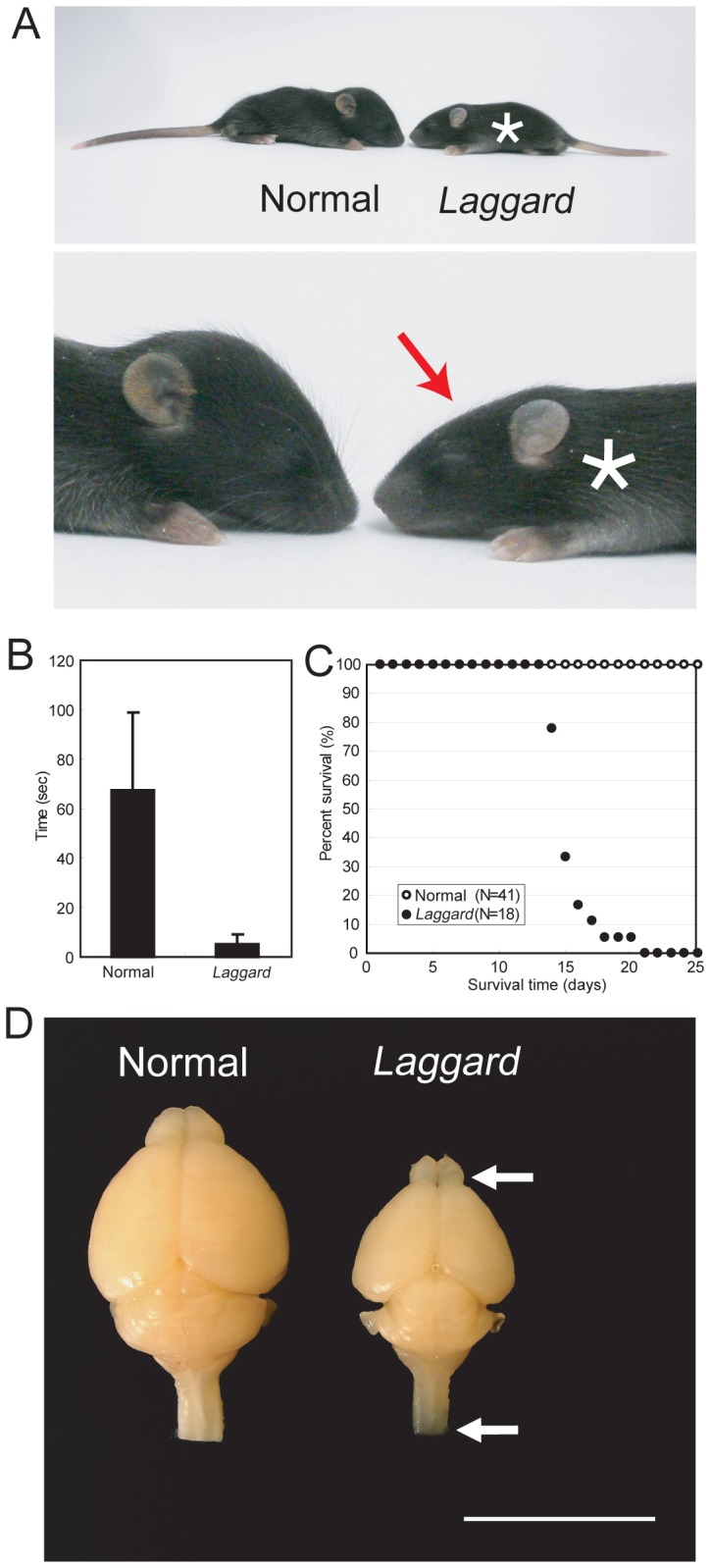
(A) The lag mutant phenotype. The littermate normal control mouse and the lag mutant mouse faced each other. Upper panel: general appearance. Lower panel: enlarged head image. Asterisk indicates the mutant mouse and red arrow indicates the flat head of the mutant mouse. (B) Behavior test for ataxia. Quantitative analysis of the duration the littermate normal control mice (n = 16) and the lag mutant mice (n = 16) stood on a narrow platform. Error bars represent SD. (C) Survival curves. Survival rate of the littermate normal control mice (open circles, n = 41) and the lag mutant mice (closed circles, n = 18) from postnatal day 1 (P1) to P25. (D) Whole brain images of the littermate normal control mouse and the lag mutant mouse at P12. Arrowheads indicate the translucent olfactory bulb and spinal cord of the lag mutant brain. Bar, 10 mm.
