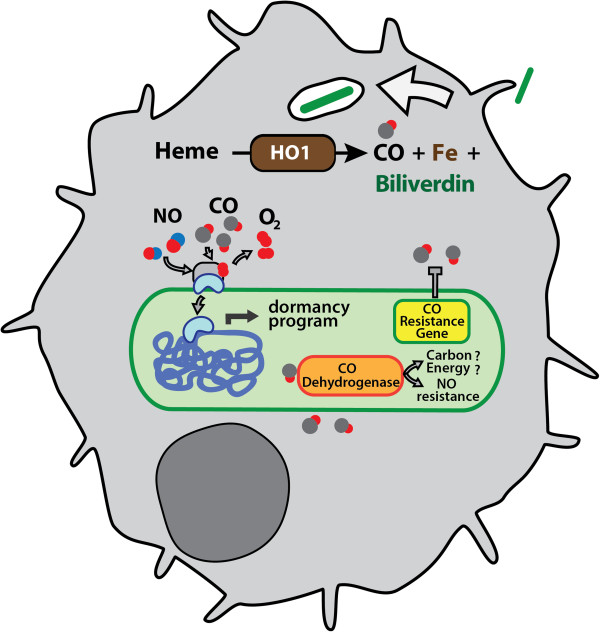
Figure 1.
Role of carbon monoxide in M. tuberculosis pathogenesis. Macrophage infection by Mtb induces HO-1. HO-1 catabolizes heme to release CO, iron and bilverdin. CO produced by HO1 can alter Mtb gene transcription by activating the DosS/DosR two component signal transduction system to stimulate a dormancy program. CO-mediated growth inhibition is resisted by the expression of a genetically encoded Mtb gene. Some mycobacteria can catabolize CO via CO dehydrogenase for growth. Alternatively, CODH may function in resisting host-derived nitric oxide.