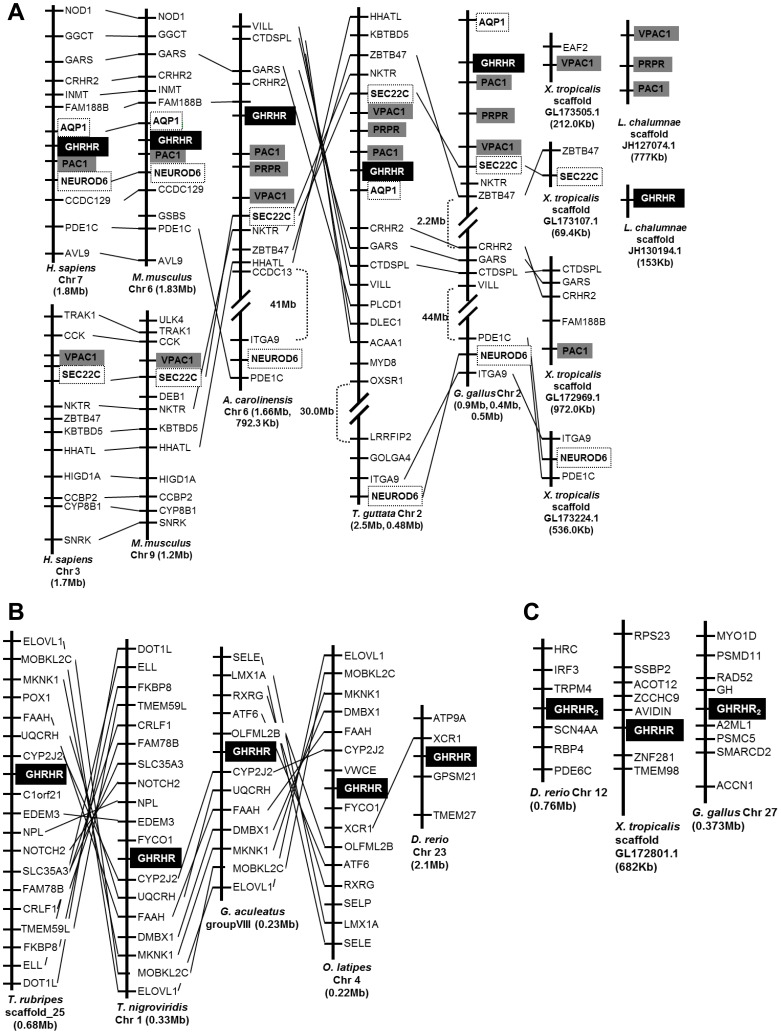
Figure 4. Gene linkage comparisons of GHRHRs in the Osteichthyes lineage.
Genes in vicinity of GHRHR were mapped, and syntenic genes were linked by straight lines. Size of the chromosomal region analyzed was given underneath based on the current edition of Ensembl databases. Syntenic genes encoding other secretin GPCR receptors were drawn in grey boxes, and the conserved flanking genes of GHRHR were drawn in closed boxes. (A) Gene environment of GHRHR in the Sarcopterygii lineage represented by human, mouse, lizard, chicken, frog and coelacanth was compared. Despite the syntenic genomic locations of GHRHR and neighbouring genes from human to avians, GHRHR was not located in frog. (B) Gene environment of GHRHR in the Actinopterygii lineage represented by fugu, tetraodon, stickleback, medaka, and zebrafish. Apart from the less conserved genomic region of zebrafish GHRHR, genes in proximity of other teleost GHRHRs were highly syntenic. However, they displayed an entirely different gene environment when compared to the sarcopterygian GHRHRs. (C) Genomic location analysis of xGHRHR characterized in present work and GHRHR2 in zebrafish and chicken. Gene synteny could neither be identified inter-species nor between the two GHRHR genes in the same species. The figures were not drawn to scale.