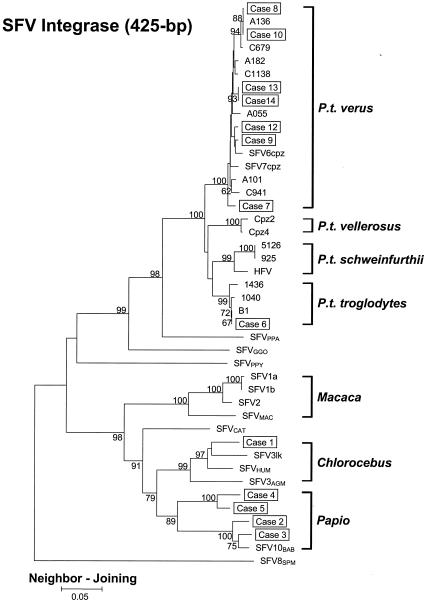
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic relationship of integrase sequences of SFV-infected workers and NHPs. The tree was derived by NJ analysis using 2 Kimura distances. The 13 cases of SFV infection are boxed. Samples were not available from subject 11. The subspecies origins for all 14 chimpanzee SFV sequences (B1, 1040, 1436, 1016, 1058, Cpz2, Cpz4, C941, A101, A055, C1138, A182, C679, and A136) are indicated. Virus origins: SFV6cpz and SFV7cpz, common chimpanzees (subspecies unknown); SFV1a, SFV1b, SFV2, and SFVMAC, macaques; SFV3AGM and SFV3lk, African green monkeys; SFVHUM, SFVAGM-infected human; SFVCAT, sooty mangabey (C. atys). Values on branch nodes represent the percentages of 1,000 bootstrap replicates, and only values greater than 60% are shown. The scale bar represents an evolutionary distance of 0.05 nucleotide per site. Trees were rooted by using the New World spider monkey (SFV8SPM) sequence.