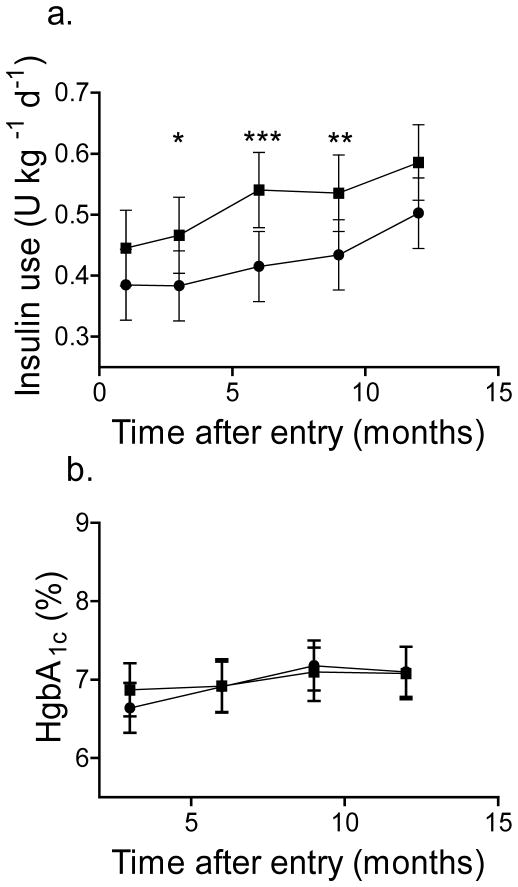
Fig. 4.
Insulin use and HbA1c levels in participants treated with teplizumab and placebo. (a) The total daily insulin use (mean±95% CI), adjusted for baseline and stratum was compared in all participants treated with teplizumab (n=31, circles) and placebo (n=27, squares). There was a significant effect of drug treatment on insulin usage (p=0.014) (*p<0.05, **p<0.02, ***p<0.01 teplizumab vs placebo). (b) The HbA1c levels, adjusted for HbA1c at study entry (mean±95% CI) in all participants are shown. The drug treatment did not have a significant effect on the HbA1c levels (p=0.67, teplizumab vs placebo). To convert values for HgbA1c in % into mmol/mol, subtract 2.15 and multiply by 10.929