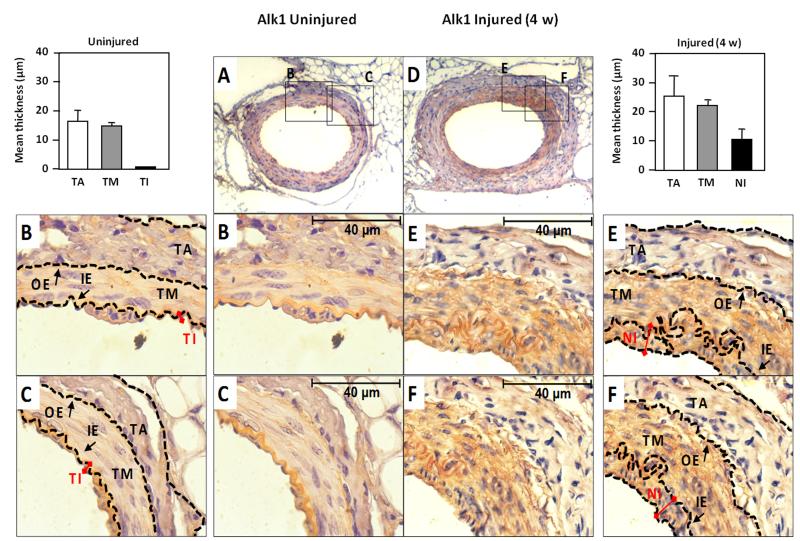
Figure 1. Alk1 expression is upregulated in vivo in neointima of mouse femoral artery after endothelial injury.
A, D. Immunohistochemical staining of Alk1 in mouse femoral artery in (A) control, and (D) after endothelial injury (28 days). Pictures were taken at 25X magnification. B, C, E and F. Zoom (100X) of different areas of the vessel wall in each case. The outer (OE) and inner (IE) elastica laminae, divide the vessel wall into the three regions: tunica adventitia (TA), tunica media (TM) and tunica intima (TI) as indicated. In the injured vessel wall, the TI has been replaced for a hyperplasic neointima (NI), where Alk1 expression is highly increased. The thickness of both intima layers are indicated with red connectors. The mean thickness of each layer in both control and injured arteries was measured and the data are represented in the histograms.