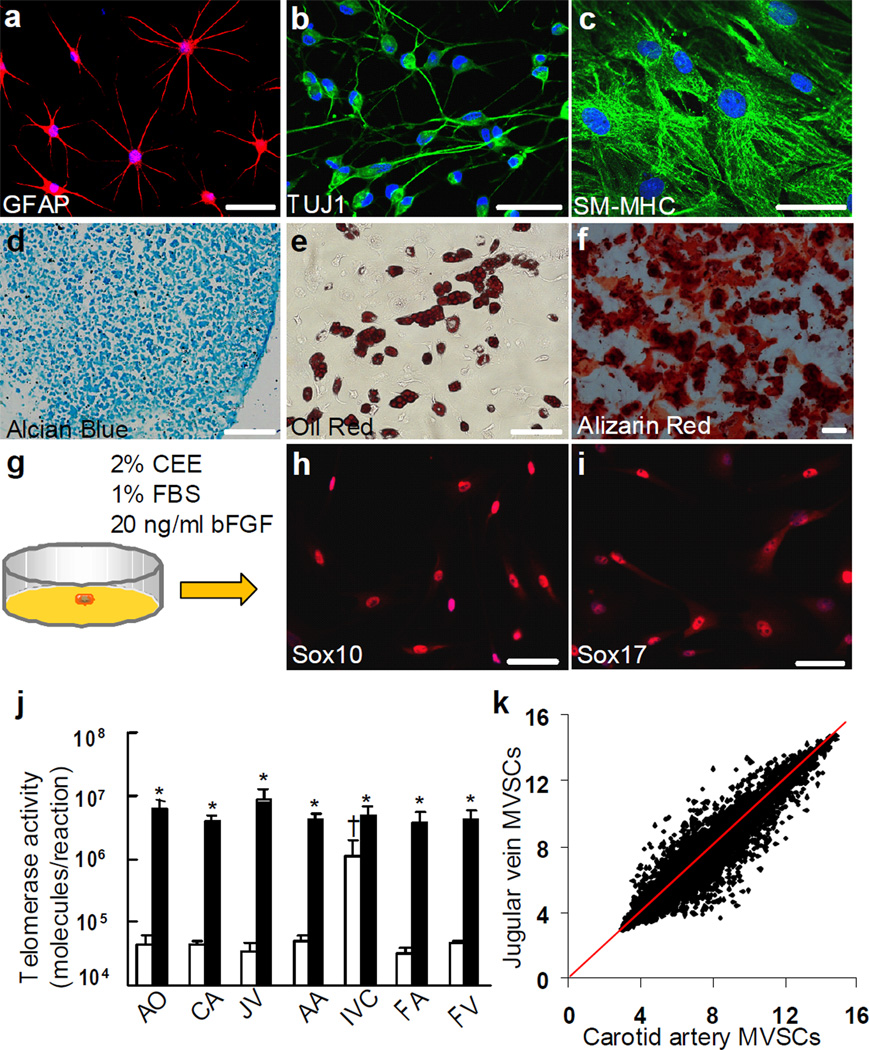
Figure 2. Differentiation assay, single cell cloning and telomerase activity assay of SM-MHC− cells derived from rat carotid arterial tunica media.
(a-f) Staining of differentiated cell derived from SM-MHC− cells: Schwann cells for GFAP (a), neurons for TUJ1 (b), SMCs for SM-MHC (c), chondrocytes for aggrecan by using alcian blue (d), adipocytes for lipid droplets by using oil red (e) and osteoblasts for calcified matrix by using alizarin red (f). Scale bars of a-c are 50 µm. Scale bars of d-f are 100 µm. (g) Schematic illustration of single cell cloning with maintenance media. (h-i) Immunostaining of cloned MVSCs for Sox10 and Sox17. (j) Telomerase activity assay of MVSCs and the tissues from which MVSCs were isolated. The data was shown as average ± standard deviation (n=3). White bars indicate tissues and black bars indicate isolated MVSCs. * indicates significant difference between MVSCs and the tissue from which the cells were derived by using Student’s t-test (p<0.05). † indicates significant difference between inferior vena cava and other blood vessels by using Holm’s t-test (p<0.05). AO: aorta, CA: carotid artery, JV: jugular vein, AA: abdominal artery, IVC: inferior vena cava, FA: femoral artery, FV: femoral vein. (k) DNA microarray analysis of MVSCs derived from rat carotid arteries and jugular veins (n=3).