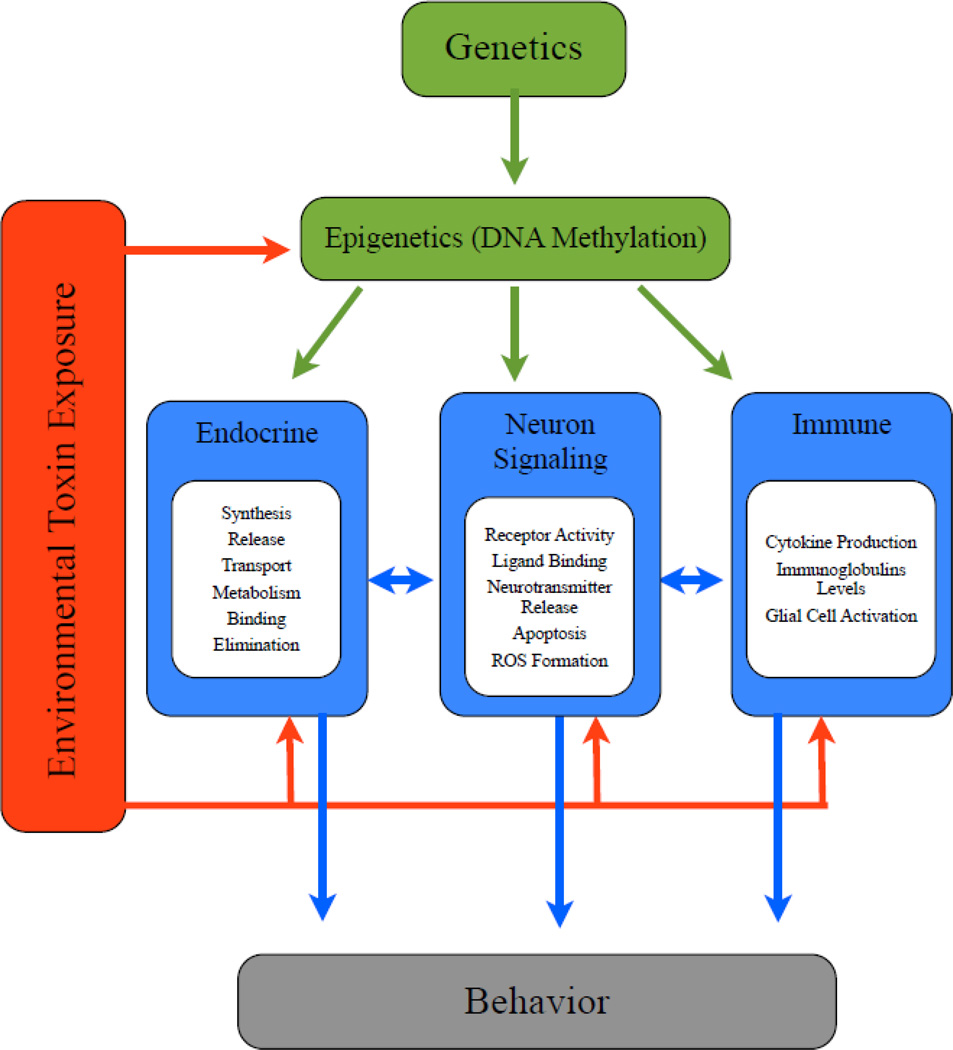
Figure 2.
Complexity of gene and environment interactions in developmental disorders. Several environmental toxins have the potential to modify gene expression via epigenetic mechanisms (e.g., DNA methylation), or by directly interfering with many critical systems for normal brain development, including the endocrine system, central nervous system, and immune system. Disruption along these pathways can result in complex behavioral outcomes, and may contribute to the etiology of neurodevelopmental disorders including autism.