Figure 3.
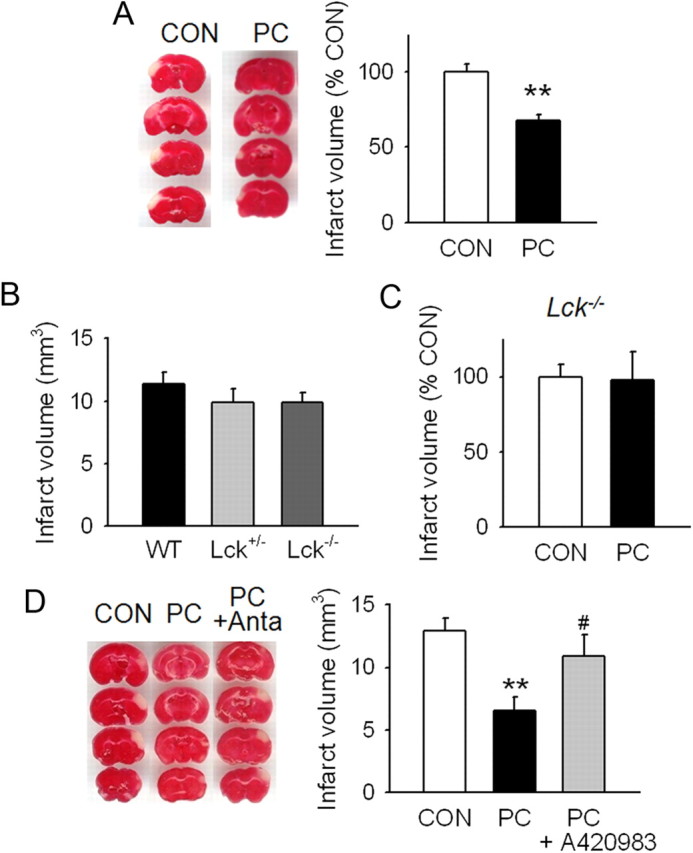
In vivo PC protection is abolished in Lck−/− mice or by Lck antagonist. A, In vivo PC was performed by exposing mice to 8% O2/92% N2 for 2 h. At 48 h after PC, the middle cerebral artery was permanently occluded for the induction of focal ischemia. Brain damage was determined by the infarct volumes at 24 h after ischemia using 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride staining. The representative brain slides are shown. B, Vulnerability to pMCAO was compared among wild-type (WT), Lck+/−, and Lck−/− mice and no significant difference was found. C, Protective effect of in vivo hypoxic PC against ischemic brain damage was not observed in Lck−/− mice. D, Lck antagonism by A420983, an orally active Lck antagonist, reversed in vivo PC neuroprotection. A420983 (18 mg/kg) was orally administered to mice immediately after PC and every 12 h thereafter for 48 h before focal ischemia. Anta, Lck antagonist A420983. **p < 0.01 versus control without PC; #p < 0.05 versus PC. A, n = 10–11; B, n = 11–15; C, n = 8–9; D, n = 14–16. All values are means ± SEM and analyzed by Student's t test.
