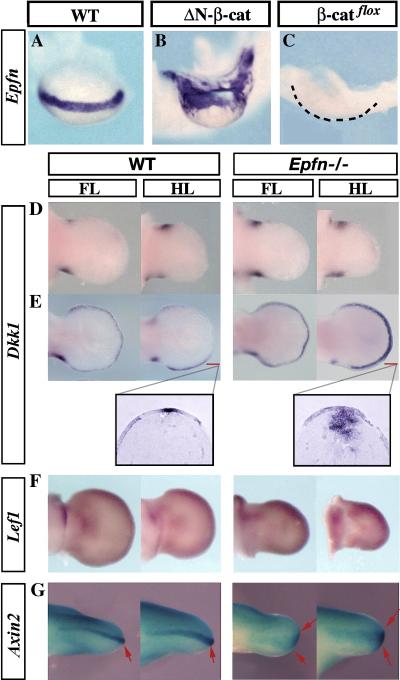
Figure 4. Epiprofin and WNT/b-CATENIN signaling.
(A–C) Whole mount in situ hybridization showing the expression pattern of Epfn in the hindlimb of wild type (A), gain-of-function mutant of b-catenin (Brn4Cre;DN-b-catenin) (B), and loss-of-function mutant of b-catenin (Brn4Cre;b -catenin flox/flox). The dashed line in (C) marks the contour of the mutant hindlimb that does not express Epfn. (D–E) Dkk1 pattern of expression is shown at E11 (top row) and E12 (bottom row) in WT and mutant limbs. Dkk1 expression is increased in the mutant distal hindlimb mesoderm as can be clearly appreciated in the longitudinal sections shown in the corresponding inserts. (F) The pattern of Lef1 expression is similar in normal and mutant limbs. (G) Axin2 expression was analyzed in compound mice expressing lacZ under the control of the Axin2 promoter. Axin2 expression is reduced in the mutant ectoderm and AER (arrows) compared with the control. Anterior views of the limbs are presented.