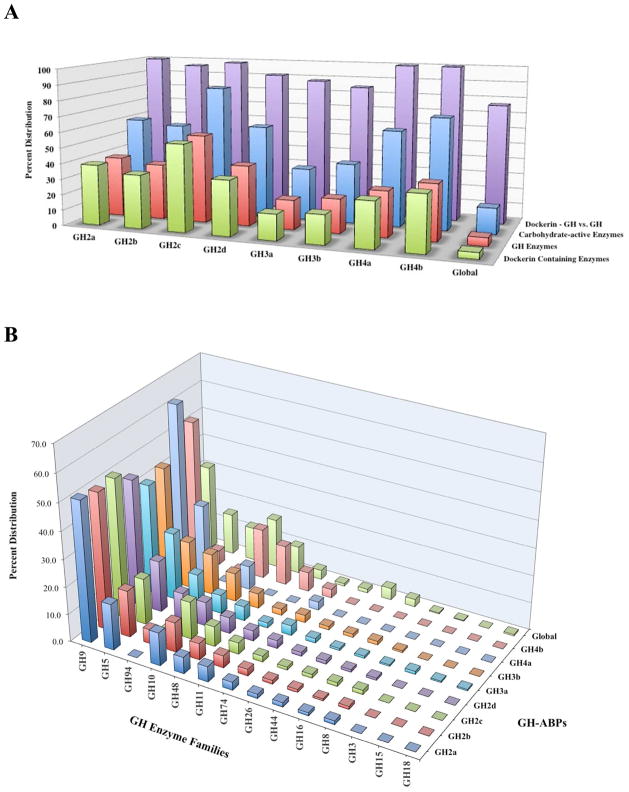
Figure 3.
(A) Percentage of total spectral counts for GH-ABP-labeled and global samples attributed to: (i) Dockerin Containing Enzymes – any enzyme containing a type I dockerin module involved in cellulosome interaction, (ii) GH Enzymes – glycoside hydrolase enzymes with and without a type I dockerin module, (iii) Carbohydrate-active Enzymes – all enzymes with and without type I dockerin modules that are active toward glycosides, including GHs, glycosyl transferases, and carbohydrate kinases. The final group, (iv) Dockerin-GH vs. GH – represents the distribution of spectral counts attributed to type I dockerin containing GH enzymes as a percentage of all measured GH enzyme spectral counts. (B) Percent distribution of total spectral counts for GH-ABP labeled and global samples attributed to glycoside hydrolase (GH) enzymes. Peptide spectral counts were averaged for each GH family; GH families were summed and distributed according to each GH-ABP. Percent distribution was calculated by dividing the average peptide spectral counts for a GH family by the total spectral counts measured for all GH families, for a particular GH-ABP. See Supporting Information for raw data. All measurements represent three sample replicates per GH-ABP.