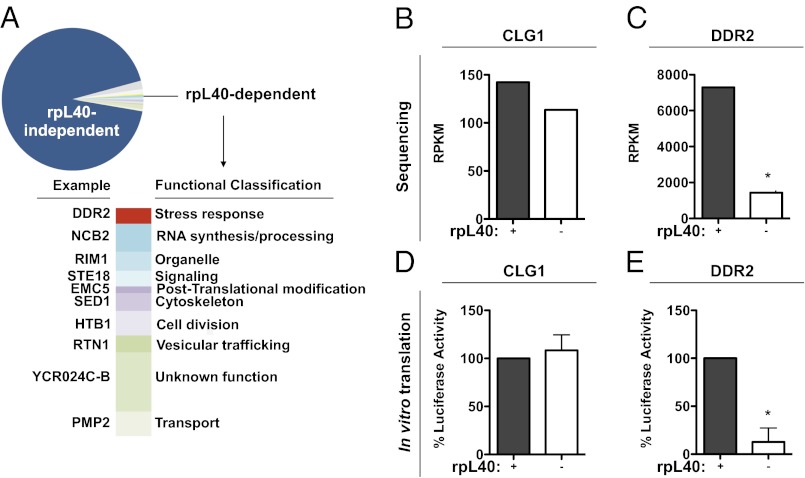
Fig. 4.
RpL40-dependent translation is used by select cellular mRNAs. (A) Functional classification of mRNAs whose polysome association is altered by rpL40 depletion. The gene in each category whose association with polysomes was most decreased by knockdown of rpL40 is listed. (B) Levels of polysome-associated CLG1 mRNA upon rpL40 depletion identified by sequencing analysis. (C) Levels of polysome-associated DDR2 mRNA identified by sequencing analysis. Average reads per kilobase of exon per million mapped reads (RPKM) from biological replicates is graphed in B and C. (D) In vitro translation of CLG1 mRNA. (E) In vitro translation of DDR2 mRNA. The results of D and E are given as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, performed in triplicate. Conditions that are statistically significant from the +rpL40 conditions are indicated with an asterisk (P < 0.0001).