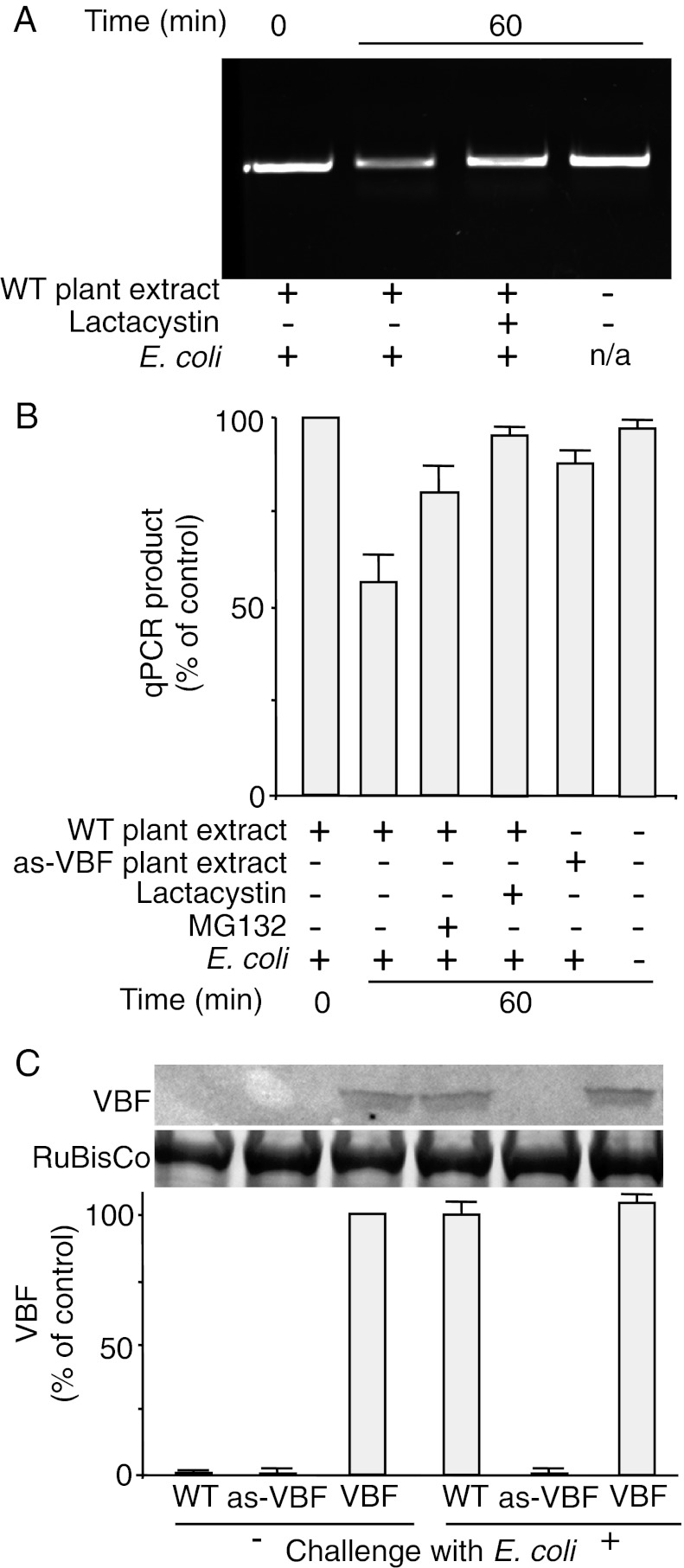
Fig. 3.
VBF promotes proteasomal uncoating of synthetic T-complexes. (A and B) Protein extracts from WT or VBF antisense plants (as-VBF) challenged for 10 h with E. coli were incubated for the indicated time periods in the presence or absence of MG132 or lactacystin with synthetic T-complexes, and the susceptibility of ssDNA to DNase I was analyzed by PCR (A) and quantified by qPCR (B). The quantified data were expressed as percent of the input signal. (C) Western blot analysis of the endogenous VBF content in Arabidopsis plants. VBF expression was induced by challenging the plants for 24 h with E. coli. (Upper) Protein extracts from WT plants, VBF antisense plants (as-VBF), or VBF transgenic plants (VBF) were analyzed with anti-VBF antibody, with putative RuBisCo large chain used as a loading control. (Lower) The resulting signal was quantified and is expressed as percent of the signal obtained in VBF transgenic, unchallenged plants. All data represent average values of three independent experiments with indicated SDs.