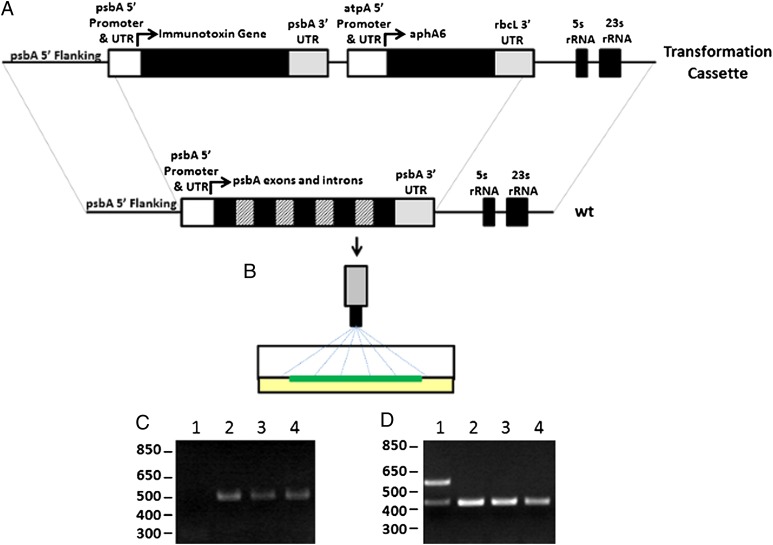
Fig. 2.
Integration of genes into the chloroplast genome by homologous recombination. (A) Immunotoxin genes are ligated downstream of the psbA promoter and 5′ UTR and upstream of the psbA 3′ UTR. This construct is placed upstream of an aphA6 gene that confers kanamycin resistance to transformed cells of algae. Regions of chloroplast genome are placed at either end of the transformation vector to allow homologous integration of the entire transformation cassette into the chloroplast genome. (B) Transformation plasmids are precipitated onto gold particles and delivered by particle bombardment into algal chloroplasts, where they recombine into the plastid genome. (C) PCR analysis using primers specific to the αCD22 scFv gene and the psbA 5′ UTR demonstrate that coding sequences for immunotoxins have been integrated into the psbA locus. Lane 1 contains PCR from WT algal cells. Lane 2 contains strains transformed with αCD22. Lane 3 contains strains transformed with αCD22-PE40. Lane 4 contains strains transformed with αCD22-CH23-PE40. (D) PCR analysis is used to confirm homoplasmicity of transformed strains of algae. Primers are used to amplify a control region of the algal chloroplast genome as well the endogenous psbA gene. Loss of the psbA gene (upper band in lane 1) demonstrates homoplasmicity of the transgenic lines.