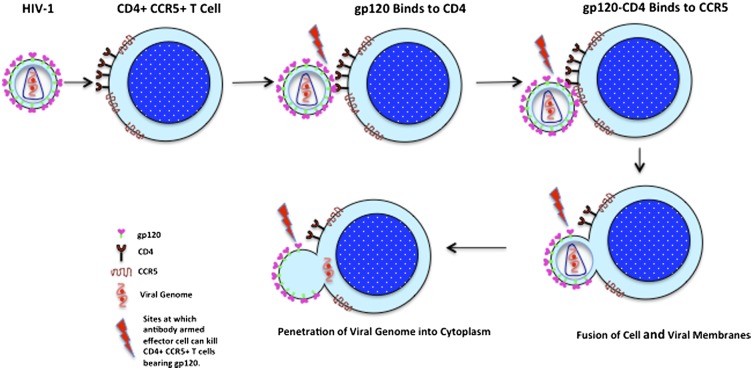
Fig. P1.
Steps during HIV-1 entry that are potential targets of antibodies that arm effector cells to kill CD4+ T cells. The gp120 domain of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env) binds to the primary receptor, CD4, on the surface of a susceptible T cell, exposing the coreceptor (CCR5) binding site on gp120, which subsequently binds to CCR5. This binding leads to further changes in Env structure, causing fusion of the viral and cell membranes and delivery of the viral genome to the cellular interior. Red lightening flashes indicate the steps at which antibodies can arm effector cells to kill CD4+ T cells via epitopes on gp120.