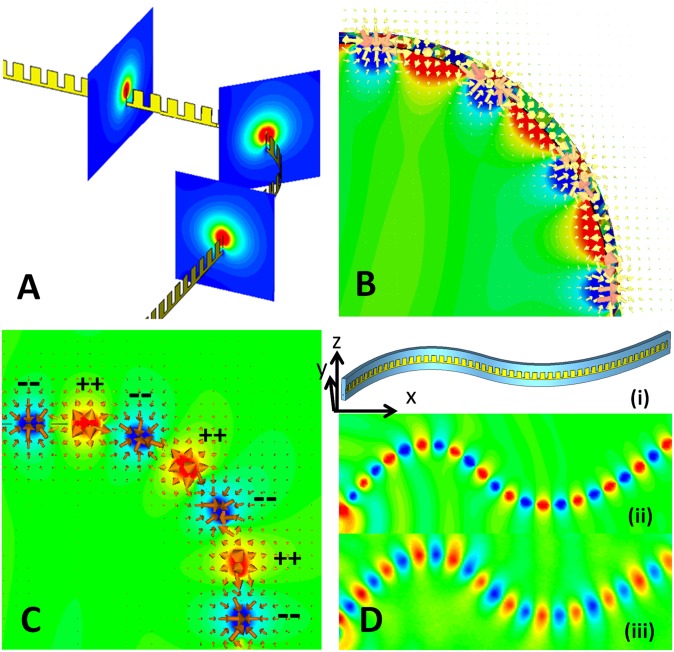
Fig. 4.
Simulation and measurement results of CSP waves on curved surfaces at 10 GHz. (A) An ultrathin corrugated metal strip (W = d, t = 0.0036d, h = 0.8d, a = 0.4d, and d = 5 mm) that is bent vertically by 90° with a bending radius of 30 mm, and numerical simulation results of power-density distributions on three different cross-sections before bending, at the bending center, and after bending. (B) 3D distribution of CSP modes across the bend, in which the arrows represent the vector E-fields and color scales indicate the field amplitudes. (C) Top view of the vector E-field distribution across the bend, clearly showing the generation of surface charges. (D) Simulation and experimental results of electric field distributions (Ez) on a vertically S-bending surface. (i) CSP structure on the S-bending surface. (ii) Simulation result. (iii) Experimental result. CSP waves creep through the bending surface smoothly. In both cases, an electric monopole pointing to the z direction is used for excitation at the left edge.