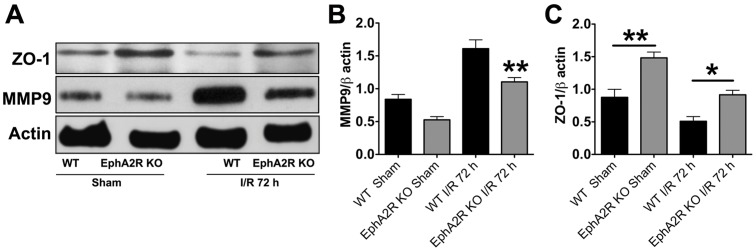
Figure 3. EphA2−/− mice demonstrate less tight junction protein disruption following focal cerebral I/R.
Cerebral I/R-induced tight junction disruption and BBB damage were analyzed with zona occludens-1 (ZO-1) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) antibodies respectively, by immunoblotting. (A and B) EphA2−/− mice demonstrate significantly lower levels of MMP-9 in I/R samples compared to the wild type group, suggestive of lower I/R-induced BBB damage. (A and C) EphA2−/− mice demonstrate significantly higher levels of ZO-1 in sham and I/R samples when compared to the wild type group, indicative of less I/R-induced tight junction disruption. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4–6. *p<0.05 or **p<0.01 relative to the wild type controls.