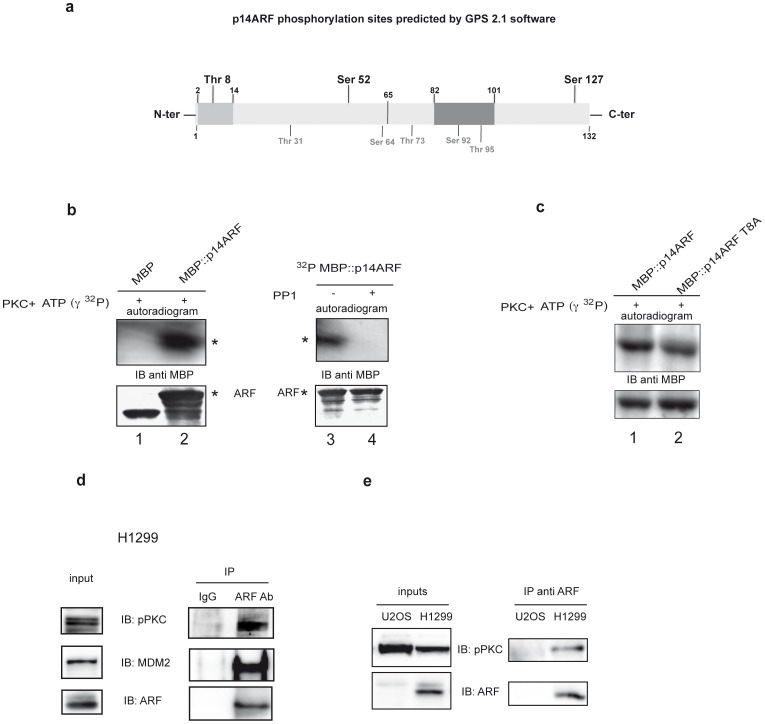
Figure 2. ARF is a substrate of PKC and PP1 in vitro.
a) Diagramatic scheme of p14ARF phosphorylation sites identified in silico. In light gray is indicated the conserved 2–14 aminoacid stretch within the N-terminal exon 1β encoded domain (aminoacid 1–65), while in dark gray the exon 2 nuclear localization signal. PKC phosphorylation sites are shown in bold above the scheme, while other kinases target sites are denoted in gray below the scheme b) In vitro phosphorylation assay. MBP (lane 1) and MBP::ARF (lane 2) were incubated with labelled γATP and catalytic PKC subunit. Reactions were then subjected to SDS-page and WB followed by ON exposure (upper panel). The lower panel shows the same filter immunoblotted with anti MBP antibodies. Detections of MBP::ARF is denoted by (*) on the autoradiograms and WBs. Purified phosphorylated MBP::ARF was divided in two aliquots and incubated (lane 4) or not (lane 3) with catalytic PP1 and processed as described in a). c) In vitro phosphorylation assay of MBP::T8A mutant. d) Co-immunoprecipitation of pPKC with ARF: H1299 lysates were incubated with anti-ARF antibody or with mouse IgG as negative control. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti pPKC Ser660, anti ARF and anti MDM2 antibodies.