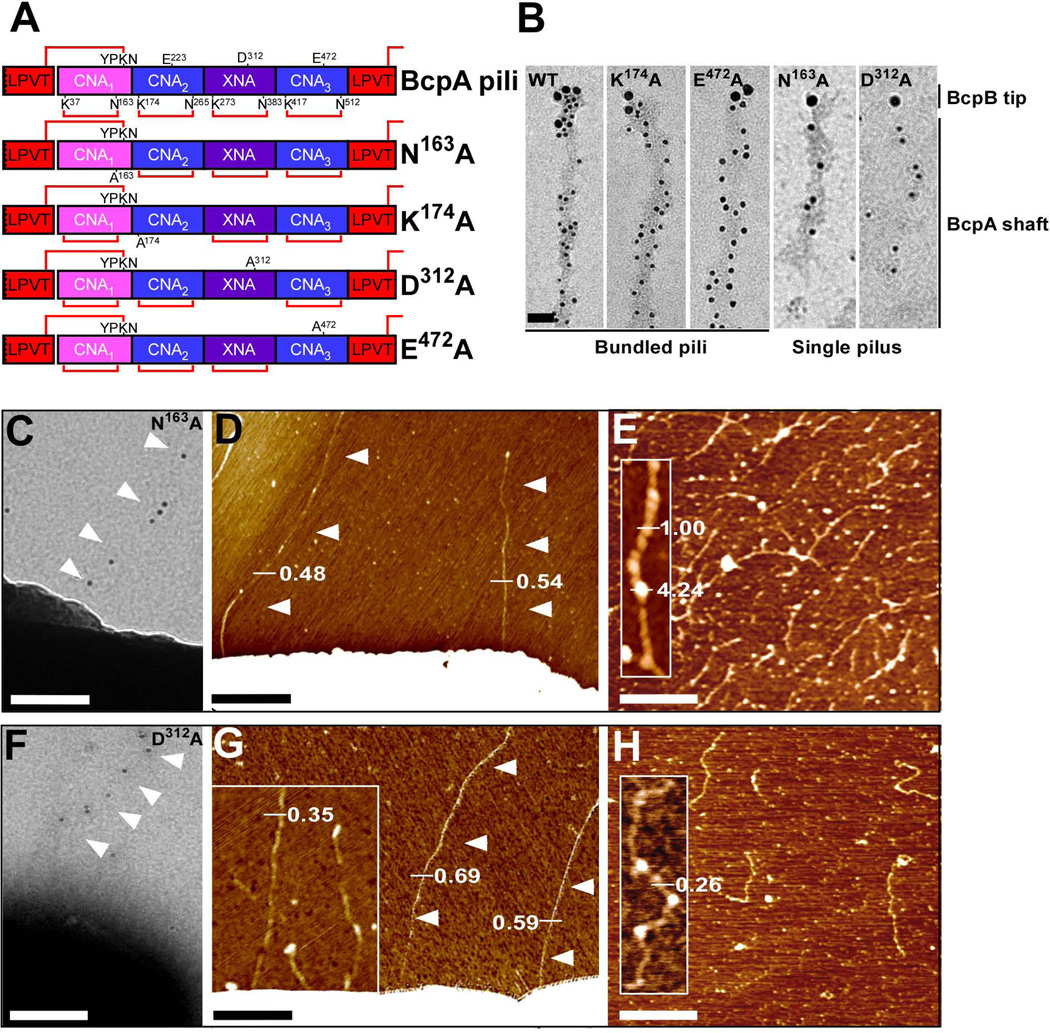
Figure 2.
Contribution of intramolecular isopeptide bonds towards pilus bundle formation. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type and mutant (N163A, K174A, D312A, and E472A) BcpA pilin that lack the CNA1, CNA2, XNA, or CNA3 intramolecular isopeptide bonds, respectively. The lysine (K) and asparagine (N) residues involved in intramolecular isopeptide bond formation (red lines) are identified. The glutamic acid (E) and aspartic acid (D) residues implicated in catalysis of the intramolecular isopeptide bonds are also identified. (B) Immuno TEM micrographs of wild-type, N163A, K174A, D312A, and E472A pili released and purified from B. anthracis Sterne srtA variants harboring pJB12, pJB109, pJB61, pJB236, or pJB107, respectively. Pili were labeled with anti-BcpB antibodies and anti-IgG-15 nm gold conjugate, fixed, and subsequently labeled with anti-BcpA and anti-IgG-10 nm gold conjugate (bar = 50 nm). (C + F) Immuno TEM micrographs in which mutant N163A and D312A pili were labeled with anti-BcpA serum followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG-10 nm gold conjugate and revealed thin pili on the surface of B. anthracis Sterne (pJB109 and pJB236) cells (bar = 100 nm). (D + G) AFM analysis of B. anthracis Sterne (pJB109 and pJB236) cells producing N163A and D312A pili revealed only single pili as indicated by height measurements in nanometer. (E + H) AFM analysis on N163A and D312A pili released and purified from B. anthracis Sterne srtA (pJB109 and pJB236) showed single filaments with unique structure. Insets, close-up of single filaments.