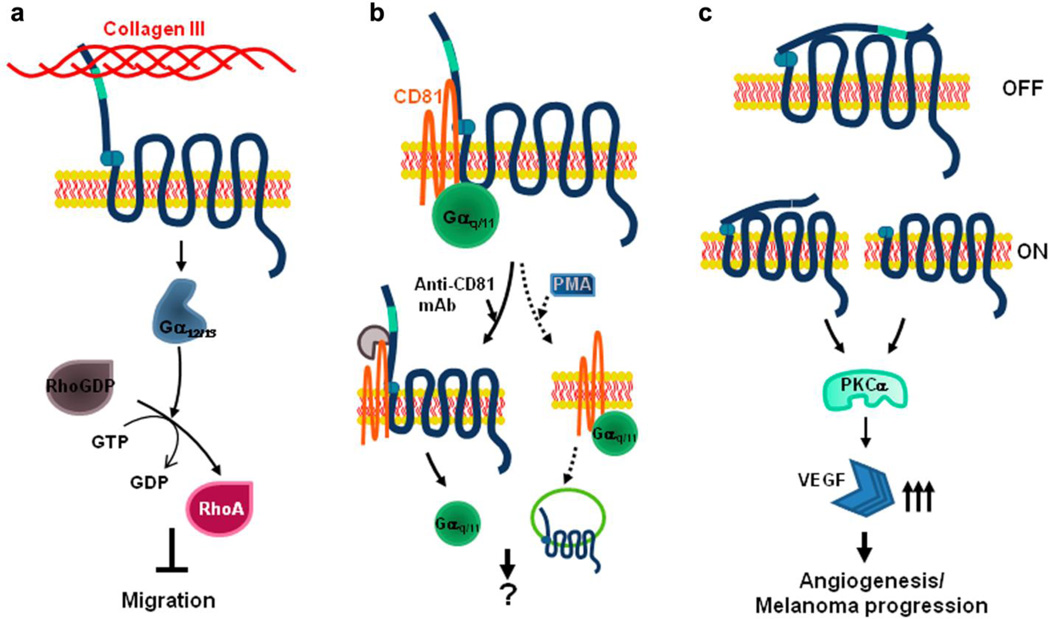
Fig. 5.
Schematic diagram of GPR56 signal pathways. a Collagen III-mediated RhoA activation. The binding of collagen III and GPR56 couples to Gα12/13 and leads to the activation of RhoA. This signaling cascade contributes to the inhibition of neuronal migration. b GPR56/CD81/Gαq/11 signaling complex. Tetraspanins CD9/CD81play a role as scaffolding proteins and stabilize GPR56/CD81/Gαq/11 complex. This complex is disrupted when CD81 protein is engaged with its antibody resulting in the separation of Gαq/11 from the complex. The complex can also be dismantled upon phorbol ester (PMA) stimulation, which results in the internalization of GPR56 (adapted from [81]). c Role of GPR56 in angiogenesis and metastasis. After cleavage, GPR56N and GPR56C form heterodimers to maintain the signaling “off” state. However, the state is switched to “on” state when “free” GPR56C is increased by GPR56C overexpression or deletion of STP segment. This “free” GPR56C activates protein kinase Cα (PKCα), resulting in increased production of VEGF, thus promoting angiogenesis and tumor progression (adapted from [38])