FIGURE 4.
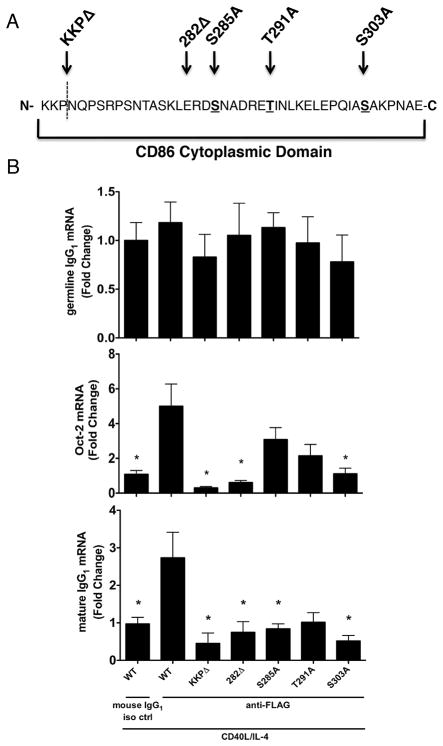
The cytoplasmic domain of CD86 also plays a role in mediating the effect of CD86engagement on B cell function. A, A series a single-alanine point mutations (S285A, T291A, S303A) or cytoplasmic truncations (KKPΔ and 282Δ) were introduced into a FLAG-CD86 expression plasmid. B, Either WT FLAG-CD86 or mutant/truncated plasmids were transfected into CH12.LX B cells before the cells were primed with CD40L/IL-4. Cells were cultured for 16 hours before an anti-FLAG Ab (M2) or species- and isotype-matched control Ab (mouse IgG1 iso ctrl) was added to the culture. 24 hours and 4 days later, respectively, the level of germline IgG1/Oct-2 mRNA and mature IgG1 mRNA was determined by qRT-PCR. Values were normalized to actin and data are expressed as mean Fold Change ± SEM relative to WT mouse IgG1 iso ctrl and represent data of quadruplicate replicates/condition from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was used to determine statistical significance relative to WT anti-FLAG. *, p < 0.05.