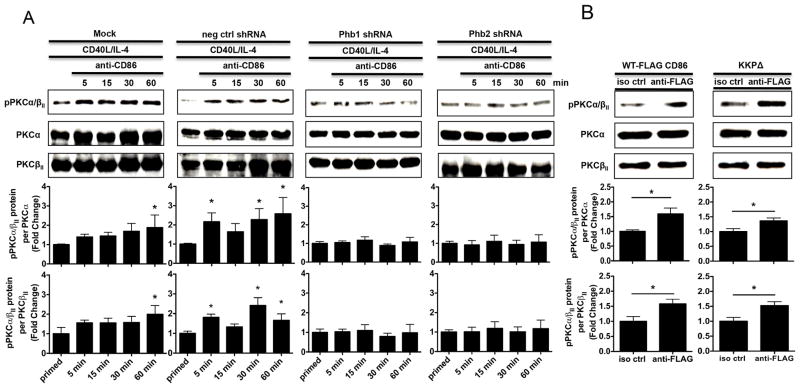
FIGURE 6.
Phb1 and Phb2 are necessary for the CD86-induced activation of PKCα/βII. A, CH12.LX B cells were either Mock transfected, with a scrambled negative control shRNA (neg ctrl shRNA), or with Phb1 or Phb2 shRNA plasmids into CH12.LX B cells via nucleofection for 24 hours followed by priming with CD40L/IL-4 for 16 hours. A CD86 Ab (anti-CD86) was administered for 5, 15, 30, and 60 minutes. Levels of phospho-PKCα/βII (pPKCα/βII) protein relative to total PKCα and PKCβII were measured via immunoblot. B, WT, and CD86 cytoplasmic-deficient (KKPΔ) FLAG-CD86 plasmids were transfected into CH12.LX B cells via nucleofection and primed with CD40L/IL-4 for 16 hours. Either an anti-FLAG Ab, or species-and isotype-matched control Ab (iso ctrl Ab) was added for 30 minutes. Levels of pPKCα/βII protein relative to total PKCα and PKCβII were measured via immunoblot. Representative gels are shown from three independent experiments. Densitometry was performed and measured pPKCα/βII relative to PKCα and PKCβII band intensity and the data are presented as the mean Fold Change in pPKCα/βII from primed B cells where CD86 was engaged relative to priming alone (A) or iso ctrl Ab (B) and expressed as the mean Fold Change ± SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical differences are shown relative to Mock priming alone (A) or iso ctrl Ab (B). *, p < 0.05.