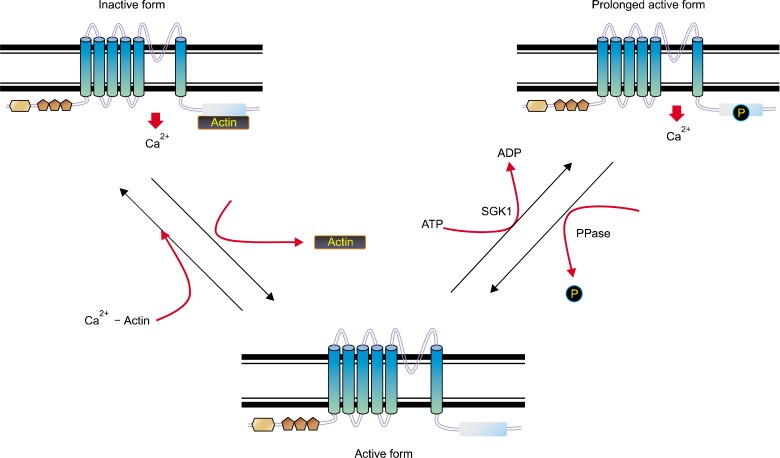
Figure 3.
The scheme of proposed TRPV4 functional regulation. TRPV4 can be modulated by the putative dual (activator/inhibitor) function protein (such as F-actin or microtubule) association/dissociation from its C-terminal cytoplasmic domain (activation/inactivation) phosphorylation. After receiving a growth signal from outside, the protein kinase such as SGK1 is activated. The protein-protein interaction between TRPV4 and (F-actin or tubulin) appears to be modulated by phosphorylation on its 824 serine residue by protein kinases (right). The active TRPV4 seems to be inactivated by protein phosphatases via dephosphorylation on its Ser 824 residue (left). The inactivated TRPV4 seems to bind with tubulin (Chun et al., 2012).