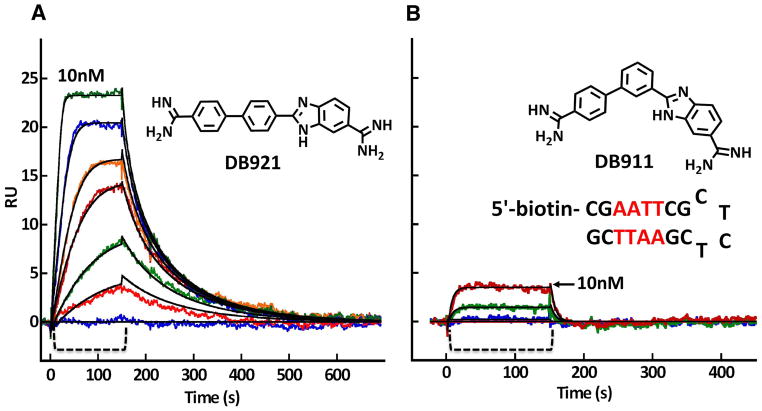
Figure 6.
In a Biacore T100 biosensor surface plasmon resonance (SPR) instrument, the DNA hairpin shown in the figure was immobilized on a Biacore SA streptavidin coated sensor chip by biotin capture. After cleaning the instrument and chip with standard protocols (Nanjunda et al., 2011), buffer flow was started until a stable baseline was obtained. To monitor the compound-DNA association reaction, DB921 (A) and DB911 (B) was then injected over the DNA surface (the bracket region in both panels) at concentrations from 1- 100 nM and binding was monitored by the change in SPR signal (RU) observed in real time. After sample injection, buffer flow was again started and the dissociation reaction was observed. Fitting these curves with a global 1:1 kinetic fit model (black lines through the curves in both panels) provides the association and dissociation rate constants and the equilibrium constants for binding of both compounds (Nanjunda et al., 2011). The binding in the Figure is only shown to 10 nM to illustrate the much stronger binding of DB921. The flow rate in the experiment was 100 μL/min at 25 °C and 0.01 M MES buffer at pH 6.5 with 0.2 M NaCl.