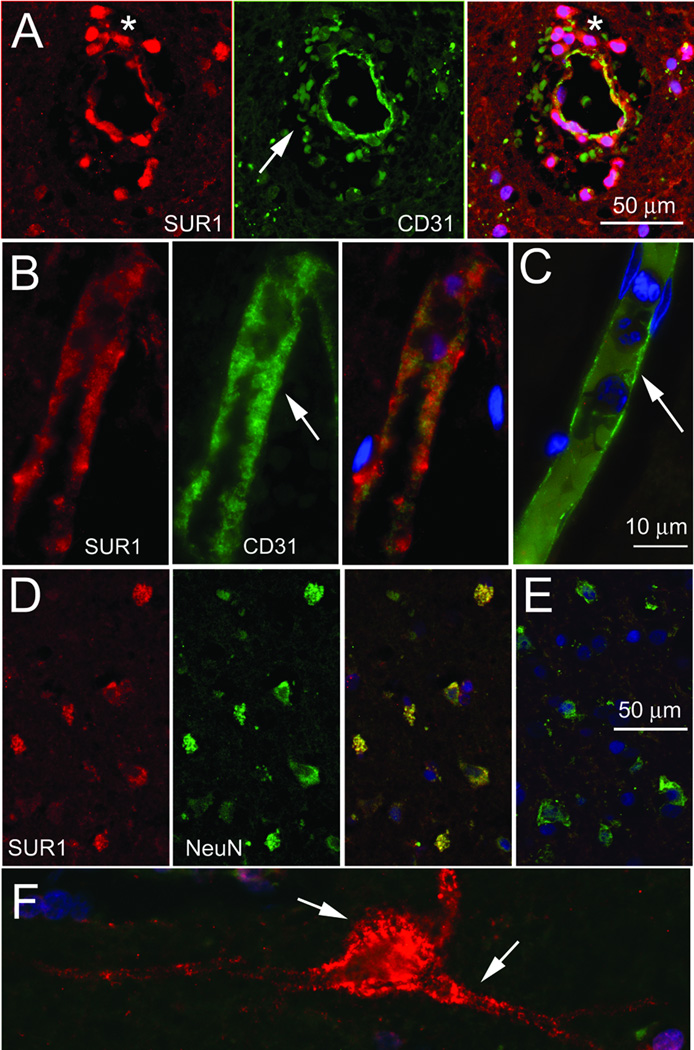
Figure 2. Sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) is upregulated in a patient with symptomatic hemorrhagic transformation (sHT).
A–C: Sections of cortex obtained at operation from the ipsilateral cerebral cortex of a patient who underwent decompressive craniectomy for malignant cerebral edema complicated by sHT (A), or at autopsy from the ipsilateral (B) and contralateral (C) cerebral cortex of a patient who had suffered a recent non-fatal embolic stroke (control), double immunolabeled for SUR1 (red) and for the endothelial cell marker, PECAM-1 (CD31; green); merged images of the double labelling are shown in (C), and in the panels on the right in (A) and (B), with co-localization indicated by the yellow colour. In (A), note the extravasated erythrocytes that autofluoresce in the green channel (arrow), and the extravasated neutrophils (asterisk) which are believed to express SUR1-KATP channels31 surrounding the SUR1-positive vessel (yellow). In (B) and (C), note the swollen SUR1-positive endothelium (B, arrow), compared to the thin, SUR1-negative endothelium in the control tissues (C, arrow). D–F: Sections of cortex from the patient with sHT (D,F) and from the control tissues (E), double immunolabeled for SUR1 (red) and for the neuronal marker, NeuN (green); merged images of the double labelling are shown in (E), and in the panel on the right in (D), with co-localization indicated by the yellow colour. Note the SUR1-positive cortical neurons with blebbing in (D,F), compared to the SUR1-negative cortical neurons in the control tissues (E); in (F), blebs are observed in the perikaryon and in large processes (arrows).