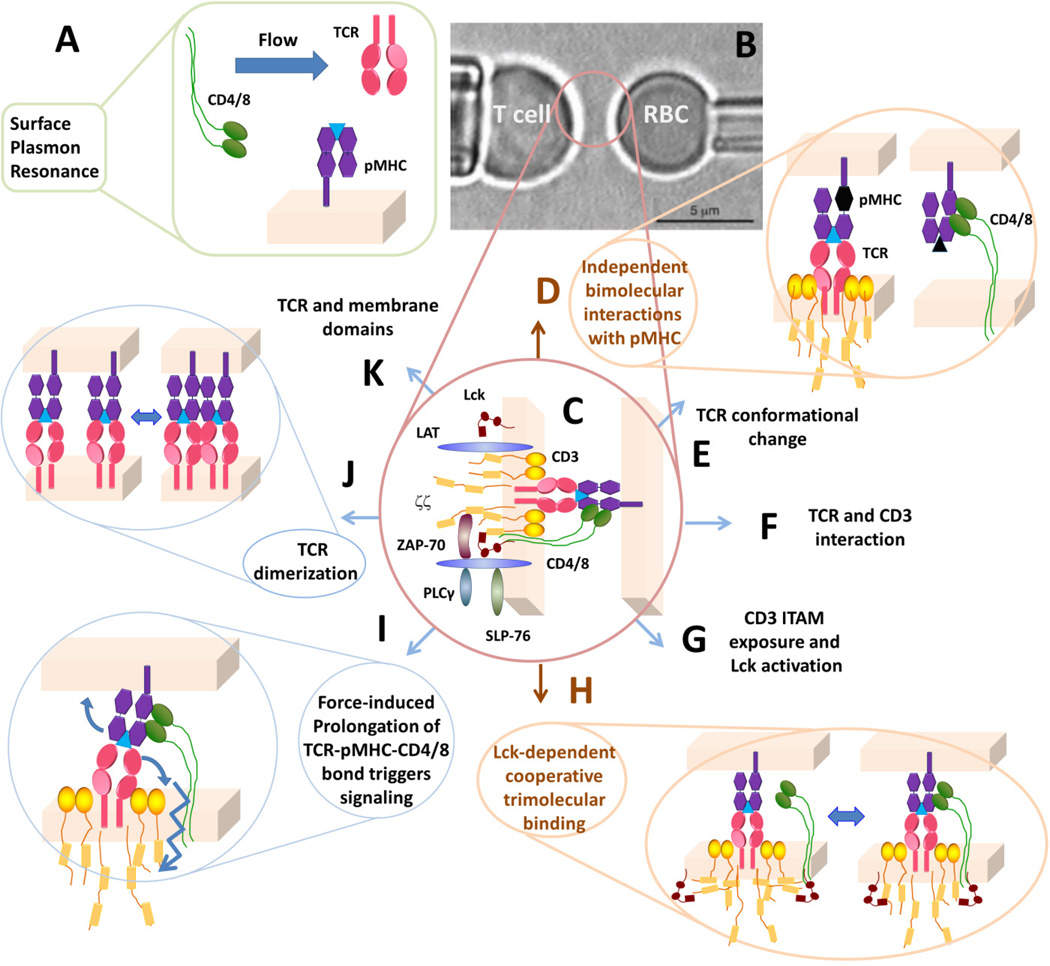
Fig. 1. Analysis of molecular interactions at the T-cell surface.
(A) Traditionally, TCR–pMHC and pMHC–CD4/8 interactions are analyzed in 3D by SPR using soluble molecules. (B) In the micropipette adhesion assay, live T cell is probed by a pMHC-coated RBC. (C) The interaction network being probed by the pMHC, including the TCR-CD3 complex, co-receptor, proximal signaling complexes formed after TCR ligand recognition. (D) Using mutant MHC to abolish co-receptor binding or null peptide to abolish TCR binding, independent TCR–pMHC and pMHC–CD4/8 bimolecular interactions can be analyzed separately. (E–G) Possible kinetic steps leading to TCR triggering. (H) Signaling-dependent cooperative binding among TCR, pMHC, and CD8. (I) Possible regulatory role of mechanical force. (J, K) Possible molecular organizations of the TCR in the membrane.