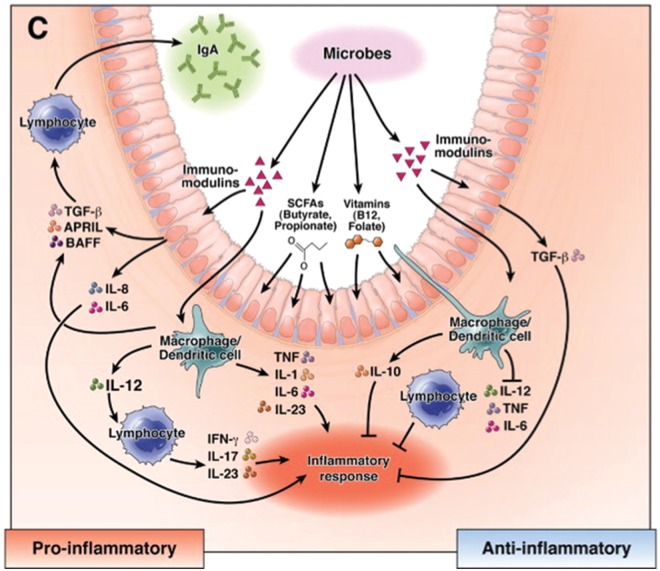
Figure 4.
Mechanisms of immunomodulation by beneficial microbes. Probiotics can modulate the immune system in the intestine through the luminal conversion process. The bacteria produce secreted soluble factors and metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and vitamins using substrates from the diet. These bioactive compounds affect the function of intestinal epithelium and mucosal immune cells, resulting in production of cytokine and related factors such as a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) and B-cell activating factor (BAFF). (Adapted from Preidis and Versalovic [2009].)