Figure 5.
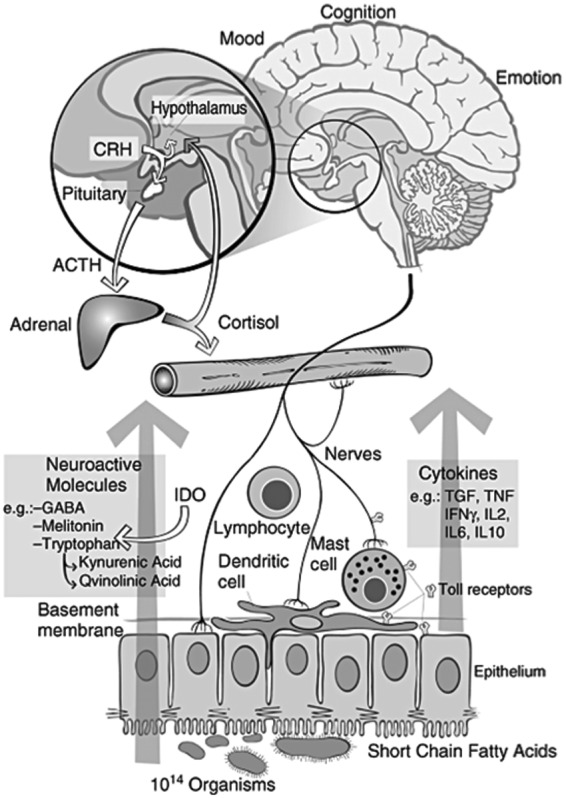
Proposed interactions between the gut microbiota, the intestinal tract, the central and peripheral nervous systems and the immune system. Intestinal microbes may interact with intestinal epithelial cells or immune cells directly or they can produce bioactive compounds and neurotransmitters to modulate immunity or the gut–brain axis. These intricate and complex interactions result in signaling to the central nervous system. CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; IDO, indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase. (Reproduced with permission from Bienenstock and Collins [2010].)
