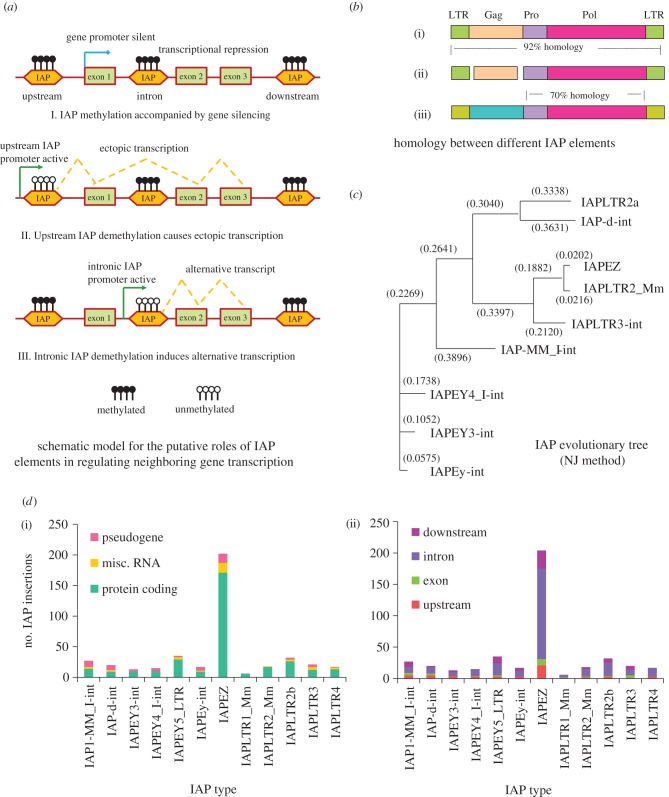
Figure 1.
Characterization of IAPs present in the mouse genic regions. (a) Schematic model to show potential IAP-mediated pathways for regulating transcription of nearby genes: (I) demonstrates the general effect of IAP insertion into a genic region. IAP elements heavily attract repressive epigenetic machineries such as DNA methylation (methylated DNA is shown with filled lollipops), which could in turn silence the transcription of nearby genes. In contrast, demethylation of an upstream IAP element could cause ectopic transcription of a gene that originates from a putative promoter element within the IAP sequence ((II); unmethylated CpG sites are shown with open lollipops); (III) exhibits the scenario where demethylation of an intronic IAP sequence could lead to ectopic splicing events. (b) Homology search performed between three IAP elements, namely, IAPLTR2_Mm (i), IAPEZ (ii) and IAPLTR3-int (iii). The IAPLTR2_Mm and IAPEZ sequences are highly similar (92% homology), while the IAPLTR3-int element exhibits approximately 70 per cent homology in the putative Pro and Pol coding regions but not in the Gag locus or the flanking LTR sites. (c) Evolutionary tree constructed by the neighbour joining method for different IAP elements used in this study. The IAPs are clustered into three putative groups, the first comprising IAPLTR2a and IAP-d-int, the second consisting of IAPLTR2_Mm, IAPEZ and IAPLTR3-int, and the last group made up of the remaining four IAP sequences (IAPEy-int, IAPEY3-int, IAPEY4_I-int and IAP-MM_I-int). (d) Bar plots showing the type of genes associated with respective IAP elements: (i) The vertical axis represents the number of insertion sites and the horizontal axis demonstrates the IAP families. The majority of the inserts were linked with protein coding genes, the rest comprising RNA-associated loci and pseudogenes. IAPEZ class of elements were the most abundant, exhibiting more than 200 inserts (approx. half of the sites identified in this study). (ii) Shows the detailed positions of the IAP insertions. Intronic insertions were predominant for all the IAP sequences.