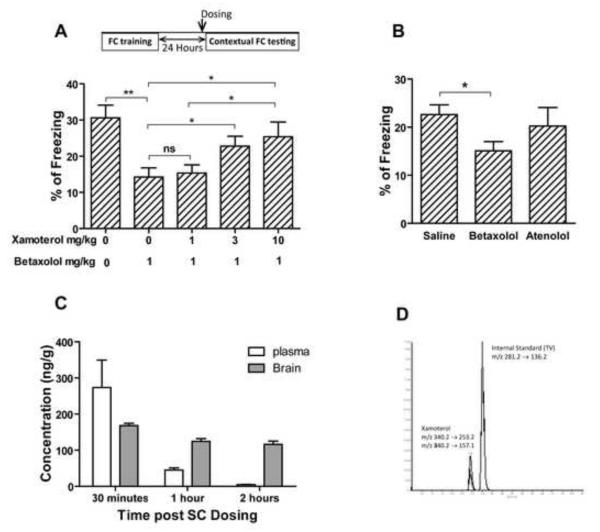
Fig. 10. Xamoterol improves the memory retrieval dose-dependently by interaction with the adrenergic receptors in central nervous system.
Betaxolol impaired memory retrieval of contextual fear conditioning in C57Bl/6J mice and xamoterol reverse the impairment dose-dependently (A). Betaxolol which can cross blood-brain barrier impaired the memory retrieval in contextual fear conditioning but atenolol which cannot get access to brain, did not have such an effect (B). n=10 for all groups in the FC tests. In all experiments xamoterol 3mg/kg, atenolol 3 mg/kg, and betaxolol 1 mg/kg were injected subcutaneously. Analyzing of plasma and brain samples showed that xamoterol can get access to blood and brain after subcutaneous injection of 3mg/kg (C and D). n=3 for each experimental groups for the plasma and brain analyzing experiment. Results are shown as Mean + SEM (ns=not significant, *=p<0.05, and **=p<0.01).