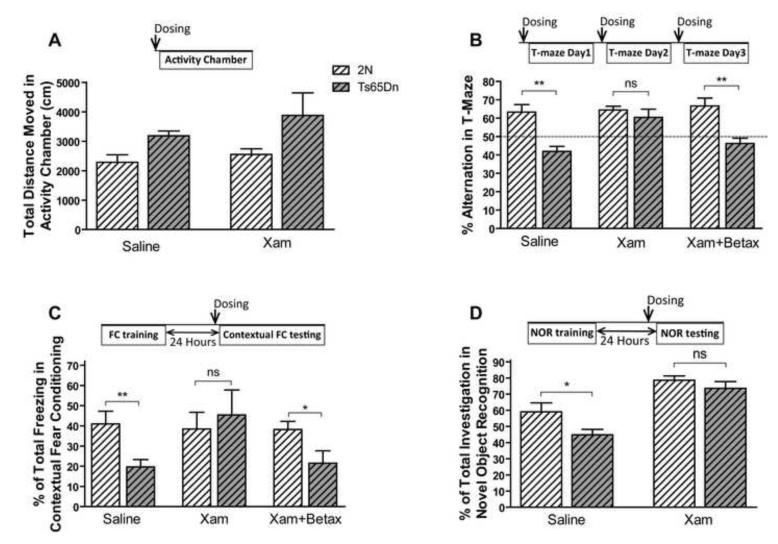
Fig. 9. Xamoterol can rescue the learning and memory in Ts65Dn mice via interaction with β1 adrenergic receptors.
Analyzing the effect of xamoterol on total ambulatory distance moved in the Activity Chamber in male Ts65Dn mice and their control littermates (A) showed no significant effect of xamoterol in both genotypes. n(2N Saline)=9, n(Ts65Dn Saline)=7, n(2N Xamoterol)=9, and n(Ts65Dn xamoterol)=9. Xamoterol rescued the spontaneous alternation deficit in male Ts65Dn mice, and betaxolol prevents its effect (B). n(2N Saline)=10, n(Ts65Dn Saline)=7, n(2N xamoterol)=9, and n(the rest of experimental groups)=8. Xamoterol also rescued the memory retrieval deficit in contextual fear conditioning in male Ts65Dn, and betaxolol prevents its effect (C). n=9 for all 6 experimental groups. Treatment with xamoterol rescued the novel object recognition deficit in male Ts65Dn mice (D). n=8 for all 4 groups. In all experiments xamoterol 3mg/kg and betaxolol 1 mg/kg were injected subcutaneously. Results are shown as Mean + SEM. Within group comparison between Ts65Dn mice and 2N mice was analyzed, and the significant differences are shown (ns=not significant, *=p<0.05, and **=p<0.01).