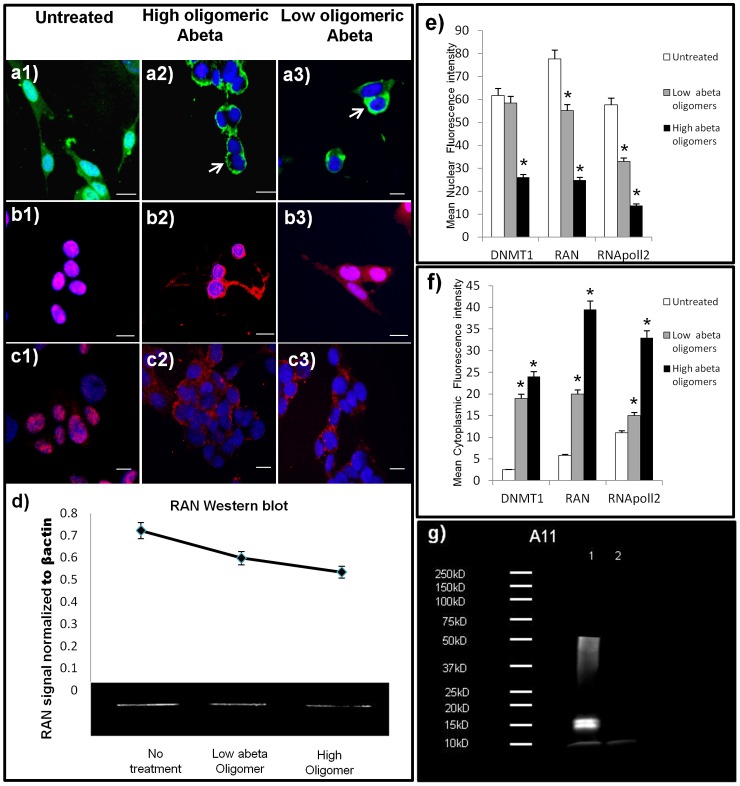
Figure 3. In vitro Aβ42 treatment replicates human neuronal distributions of nuclear proteins.
Micrographs of DNMT1 and RNA pol II in neurons (SK-N-Be(2)) treated with higher molecular weight (MW) oligomers of Aβ42 (1 uM) or lower MW oligomers of Aβ42 (1 uM) for 36 hours. High power micrograph (40X) of cultures labeled with an antibody to RAN before (a1) and after treatment with higher MW oligomeric Aβ42 (a2) or lower MW oligomeric Aβ42 (a3); shows nuclear and cytoplasmic loss with nuclear envelope accumulation (arrows), similar to that seen in vitro. Western blot analysis confirms these data of an overall reduction in basal RAN protein levels when treated with oligomeric abeta (d). Normal distributions for nuclear molecules DNMT1 (b1), and RNA pol II (c1) was readily apparent in the nucleus of untreated neurons, but translocation to the cytoplasm is seen in both molecules when treated with high or lower MW oligomeric Aβ42; Dnmt1 (b2, b3), and RNA pol II (c2, c3). e) Mean nuclear fluorescence intensity and mean cytoplasmic fluorescence intensity (f) of nerve cells treated with either low MW Aβ42 oligomers, or high MW Aβ42 oligomers. Asterisk (*) signifies a significant difference compared to control samples (p<0.05). Data are presented as mean +/− S.E.M. (g) Western blot analysis using oligomeric antibody A11, revealed the presence of oligomers in both preparations, with higher MW oligomers in lane 1 (96 hour aggregation), compared to lane 2 (immediately frozen). (Scale bars = 15 um).