Figure 1. Neural tube closure and convergent extension in the chick.
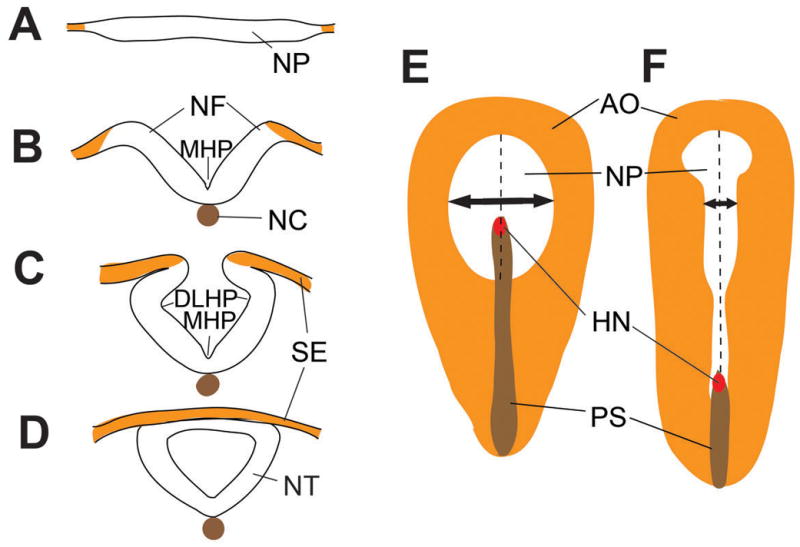
(A–D) Neural tube closure events shown in cross-sectional view. (A) Apicobasal thickening of the neural plate prior to neural tube closure (NTC). (B) Median hinge point (MHP) formation at the ventral midline of the neural plate. Note the association of the notochord (NC) with the MHP and the elevation of the neural folds (NF) above the ventral midline. (C) Formation of the dorsolateral hinge point (DLHP) and the association of the NP with the surface ectoderm (SE). (D) Dorsal midline fusion of the neural plate and SE. (E, F) Top down views of the chick neural plate, with rostral to the top and the dorsal surface facing the viewer. Convergent extension narrows and elongates the neural tube (white tissue; double headed arrow). Area opaca (AO, orange), primitive streak (PS, brown) and Hensen’s node (HN, red) are shown for orientation.
Abbreviations: AJ: adherens junctions; AO: area opaca; DLHP: dorsolateral hinge point; HN: Hensen’s node; LGL: lethal giant larva; MHP: median hinge point; NC: notochord; NF: neural fold; NP: neural plate; NT: neural tube; NTC: neural tube closure; PS: primitive streak; SE: surface ectoderm; TJ: tight junctions.
