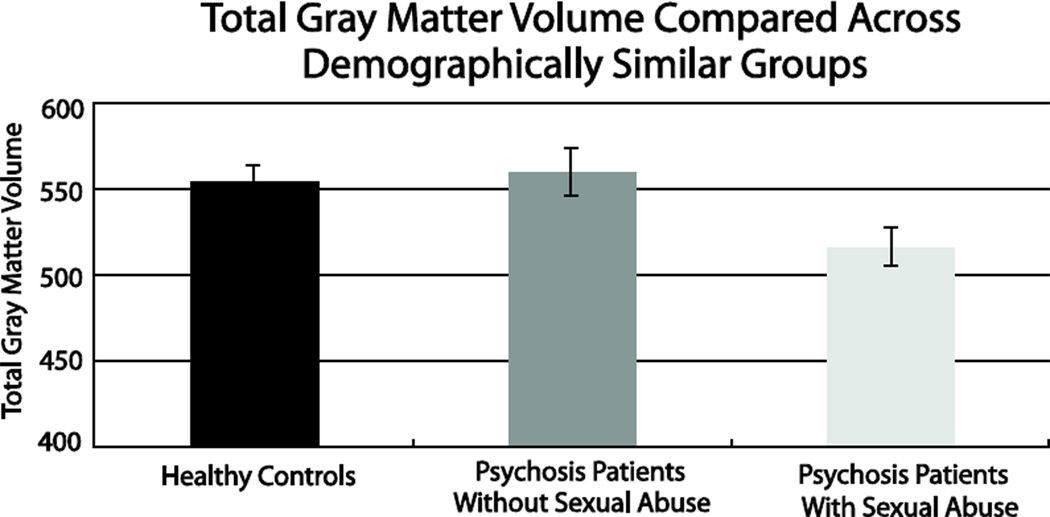
Figure 3.
In demographically matched samples, psychotic disorder patients with childhood sexual abuse (n=24) had significantly decreased gray matter volume compared to healthy controls (n=26) (t(48) = 2.3, p = .03; Cohen’s d = .63) and psychotic disorder patients without sexual abuse (n=23) (t(45) = 2.4, p = .02; Cohen’s d = .71). Psychotic disorder patients without sexual abuse did not differ in gray matter volume from healthy control subjects (t(47) = .40, p = .69).