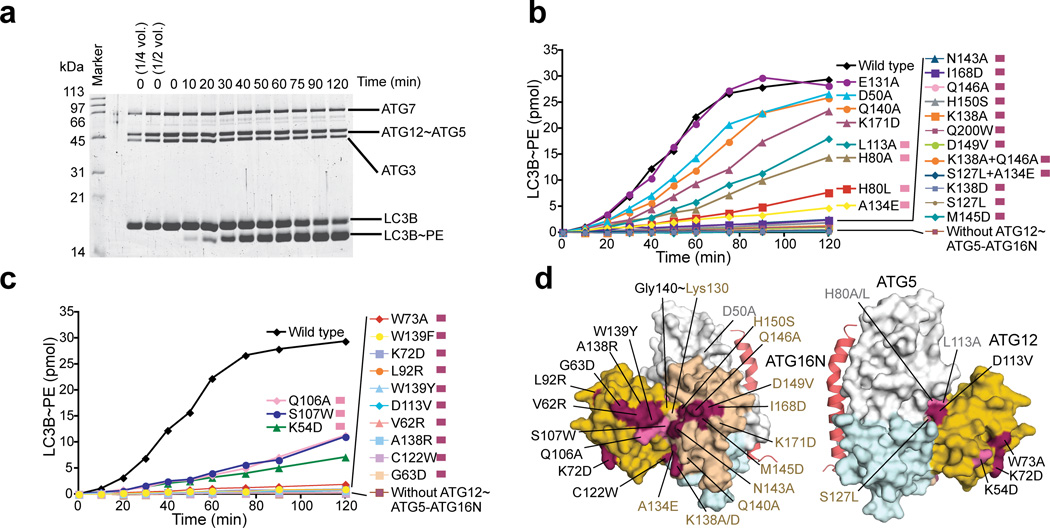
Figure 4.
Conserved residues of ATG12~ATG5 are important for E3 activity. (a) SDS-PAGE of an in vitro kinetic LC3 lipidation assay carried out with the wild-type ATG12~ATG5–ATG16N. (b and c) The quantified data of the in vitro kinetic LC3 lipidation assays carried out with ATG12~ATG5–ATG16N containing mutations in ATG5 (b) or ATG12 (c). The raw data for (b) and (c) are shown in Supplementary Figure 3. (d) Mapping of the results of the in vitro mutagenesis data onto the structure. The residues that have been affected by mutation are shown in the same color as indicated on the right side of the description for each mutation in (b) and (c).