Figure 1.
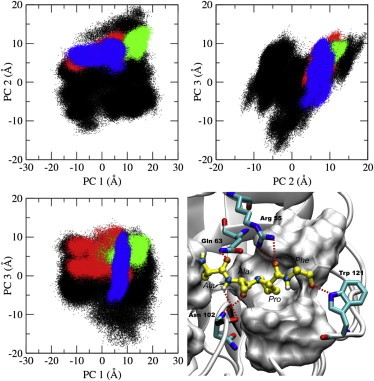
Principal component analysis (PCA) of substrate-free CypA and substrate-bound CypA complexes. The top three principal components’ dominant motions are shown, with each data point representing a conformation of the active site residues. Depicted are the substrate-free enzyme (black), the trans-CypA complex (red), the transition-state-CypA complex (green), the cis-CypA complex (blue), and the substrate-bound CypA complex with hydrophobic active-site residues (on white surface). Also depicted are the active site residues (Arg55, Gln63, and Asn102) and Trp121 that form hydrogen bonds with the substrate (sticks), and the substrate in the transition state configuration (yellow).
