Figure 6.
TRUC Disease Is Critically Dependent on IL-7R Signaling
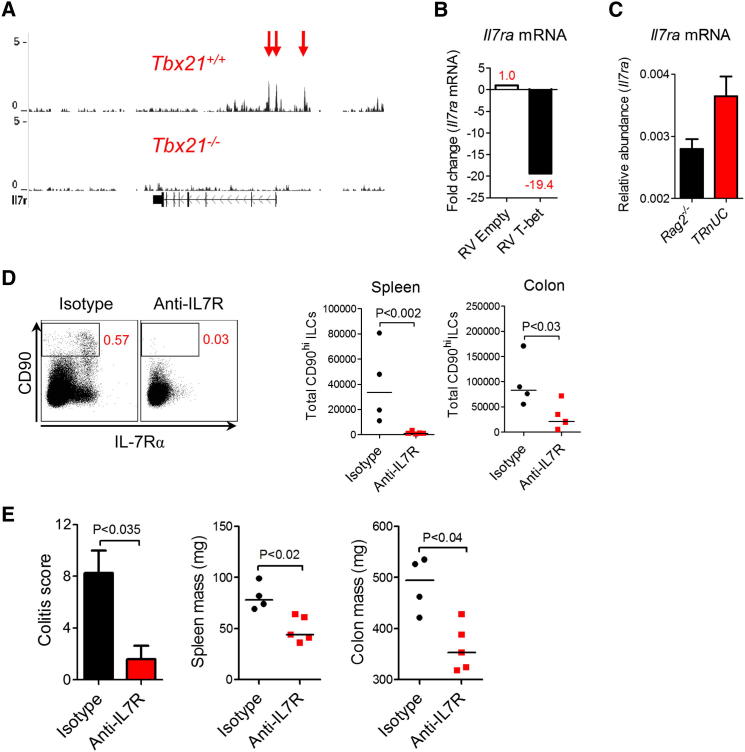
(A) UCSC Genome Browser image is shown for T-bet binding at the il7ra locus in Tbx21+/+ versus Tbx21−/− CD4+ Th1 cells following stimulation with PMA and ionomycin for 4 hr. Chromatin was immunoprecipitated, crosslinked, and prepared as described previously (Jenner et al., 2009). Samples were sequenced with an Illumina Genome Analyzer II-x. The vertical axis depicts the number of tags per million total sequences, with the genomic location running along the horizontal axis. The direction of transcription is indicated by arrows. Red arrows depict three sites of T-bet binding at the Il7ra locus.
(B) Relative abundance of Il7ra mRNA in Tbx21−/−Ifng−/− CD4+ T cells following retroviral transduction with empty vector (RV) or T-bet (T-bet RV). Cells were activated with PMA and ionomycin.
(C) Relative abundance of Il7ra mRNA in fluorescence-activated cell-sorted Tbx21−/− and Tbx21+/+ CD90hi ILCs isolated from mLN of TRnUC and Rag2−/− mice following induction of disease with anti-CD40. Results show mean, and error bars represent SEM.
(D) Representative flow cytometry plot of splenic CD90+IL-7R+ ILCs (left panel) and absolute numbers (right panel) of ILCs in the spleen and colon of TRUC mice, following treatment with anti-IL7R or control antibody.
(E) Colitis score (left panel), spleen mass (middle panel), and colon mass (right panel) in TRUC mice following treatment with anti-IL-7R or control antibody. Results show mean, and error bars represent SEM.