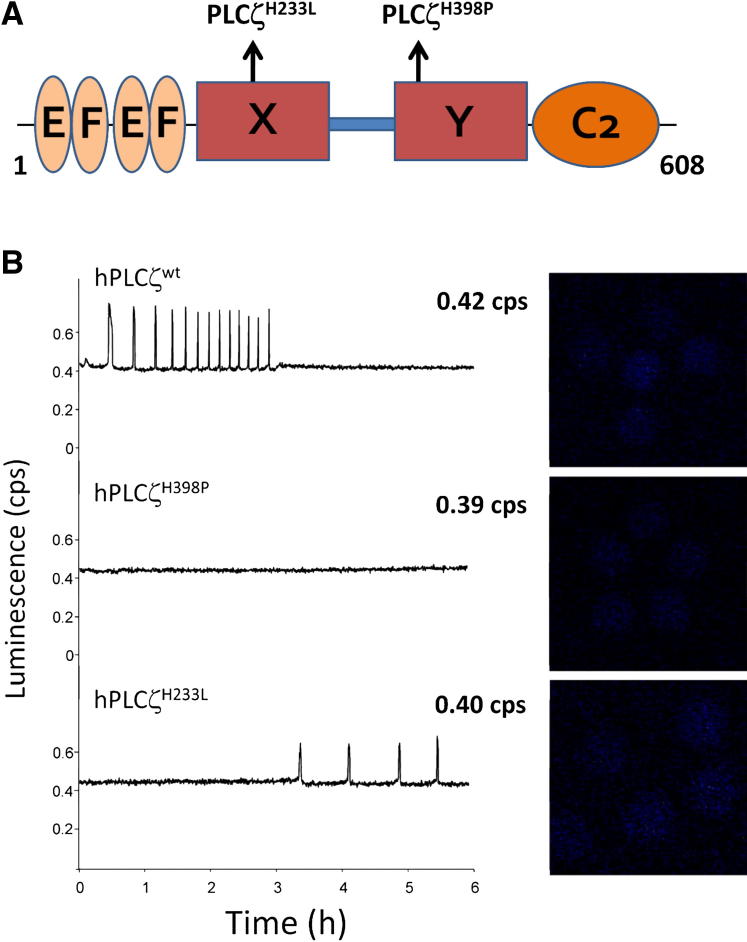
Figure 4.
Effect of H233L and H398P mutations on Ca2+ oscillation-inducing activity of human phospholipase Cζ (PLCζ) in mouse eggs. (A) Schematic representation of human PLCζ domain structure identifying the location of H233L and H398P mutations within the X and Y catalytic domains, respectively. (B) Fluorescence and luminescence recordings reporting the cytosolic Ca2+ changes (black traces; Ca2+) and luciferase-PLCζ expression level (in counts per second, cps), respectively, in unfertilized mouse eggs after the microinjection of cRNA encoding luciferase-tagged, wild-type human PLCζ, and the PLCζH233L and PLCζH398P mutants. Panels on the right display the integrated luminescence image of individual mouse eggs after cRNA microinjection of either wild-type or mutant PLCζ. The relatively low luminescence values achieved, corresponding to femtogram levels of PLCζ protein expressed in each cRNA-microinjected egg, are intended to mimic the approximate amount of PLCζ that is delivered by entry of a single sperm.