Fig. 1.
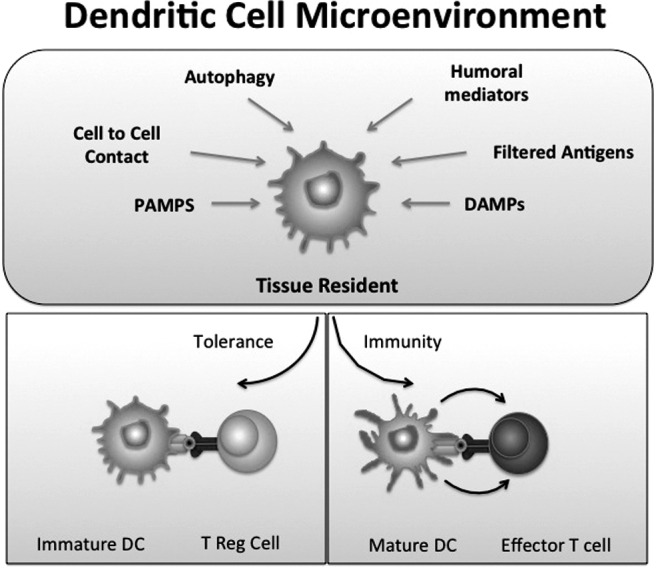
Dendritic cells (DCs) have a dual role and can induce tolerance or immunity. In the steady state, immature DCs situated in the renal interstitial microenvironment are affected by autophagy of proteins from dying cells, cell-to-cell contact, PAMPS, DAMPS, humoral mediators, or filtered antigens. In the absence of inflammatory signals these immature DCs express low amounts of costimulatory molecules and may induce tolerance. During an infection or in the presence of maturation-inducing inflammatory signals, mature DCs induce the development of effector T-cell responses.
