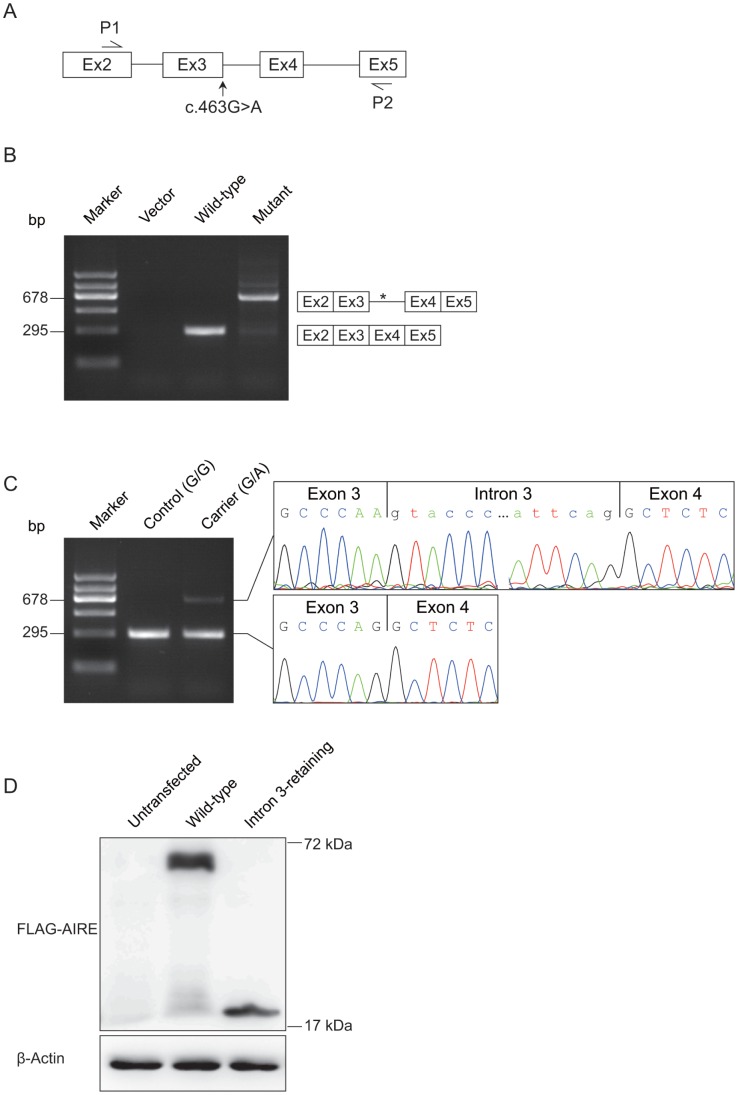
Figure 2. Alternative splicing of AIRE by the c.463G>A mutation.
(A) Schematic diagram of the AIRE minigene constructs. Complete genomic DNA spanning from exon 2 to exon 5 of AIRE gene was amplified from wild-type control and the APS-1 patient (homozygous for the c.463G>A mutation), respectively, for minigene analysis. P1 and P2 were exonic primers to evaluate the results of RT-PCR. (B) Minigene constructs were individually transfected into HeLa cells. RT-PCR products amplified with the primers (P1 and P2) showed an aberrant splicing pattern in mutant minigene compared with wild-type minigene. The predicted cDNA transcripts are shown, which was confirmed by DNA sequence analysis. * indicates the premature termination codon in intron 3. (C) RT-PCR analysis of AIRE mRNA from lymph node needle biopsy of a heterozygous carrier (III-1; G/A) and a healthy control (G/G) using the same primers of minigene analysis. A cDNA fragment of 295-bp, which corresponded to predicted wild-type transcript, was identified in both control and the heterozygous carrier of the c.463G>A mutation. In addition, a longer 678-bp transcript was identified in the heterozygous carrier. DNA sequence analysis of the 678-bp transcript revealed the retention of exon 3. (D) In vitro translation assay. Total cell lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with wild-type or intron 3-retaining AIRE were immunoblotted with FLAG antibody. Compared with the wild-type, the intron 3-retaining AIRE translated a shorted product. β-actin was used as an internal control.