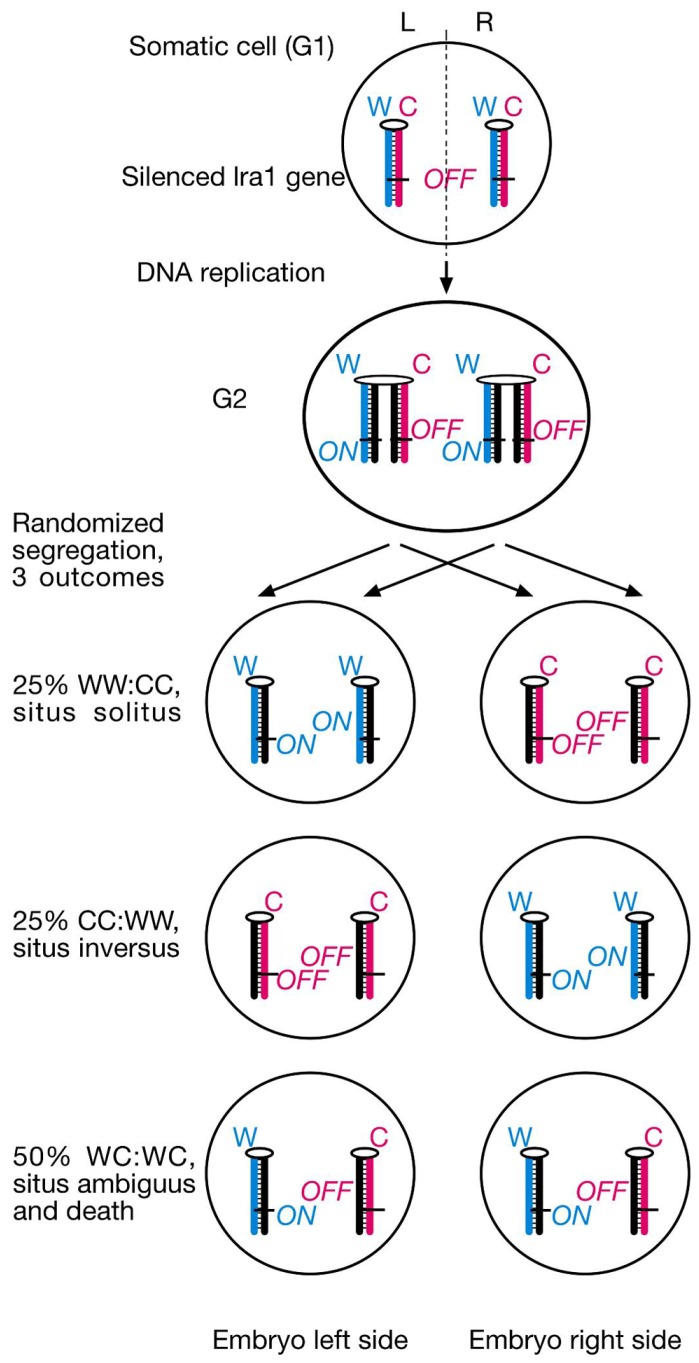
FIGURE 2.
SSIS-predictions concerning embryo situs and survival rates of lrd mutants. Proposed laterality-generating asymmetric cell division is randomized in the lrd mutant. The future L/R axis is set by cytoplasmic polarization and alignment of a single cell with respect to the anterior-posterior and dorsal-ventral body axes. Sister chromatids containing a hypothetical “leftness-encoding” left-right axis-establishing gene 1 (lra1) are epigenetically differentiated. Normally, left-right dynein would selectively segregate older Watson template strand-containing sister chromatids harboring lra1 “ON” epialleles to the left body side, and older Crick template strand-containing sister chromatids harboring lra1 “OFF” epialleles to the right body side as described in Figure 1A. Randomized segregation due to left-right dynein mutation will result in three different outcomes shown here: 25% WW:CC cell pairs, causing normal situs development, 25% CC:WW cell pairs, causing development of situs inversus, and 50% WC:WC cell pairs, causing severe developmental situs abnormalities incompatible with survival.