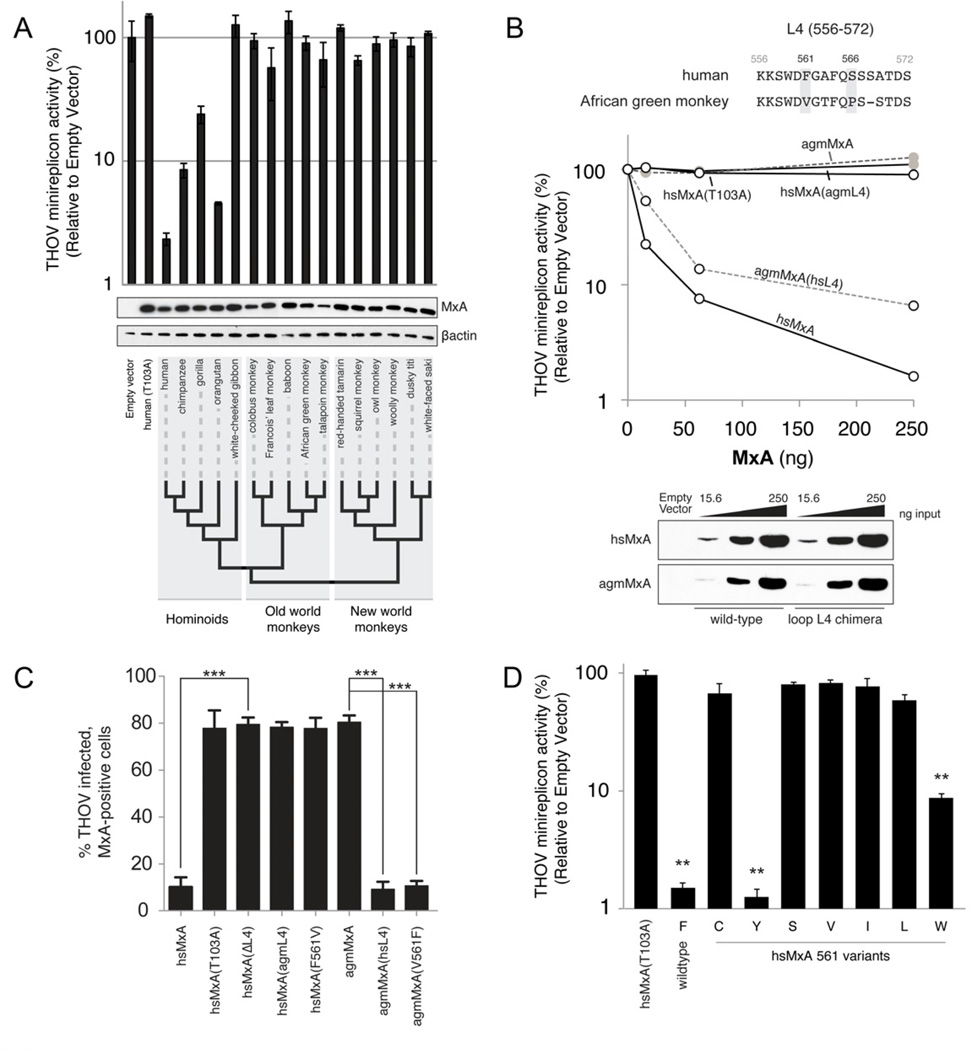
Figure 2. Species-specific antiviral activity results from sequence divergence in loop L4 of primate MxA.
A. THOV minireplicon activity (luciferase levels) was measured 24h post-transfection, and was reported relative to levels observed in the absence of MxA. hsMxA(T103A) is an antivirally inactive mutant of hsMxA. Error bars represent standard deviation across three biological replicates. HA-tagged MxA and βactin protein levels were detected in lysates by Western blot. The phylogenetic relationships of MxA derived from representative species within hominoid, old world monkey and new world monkey lineages are indicated by a cladogram.
B. Differential antiviral activity of human and AGM MxA orthologs is dependent on loop L4. The loop L4 (amino acids 556–572) protein sequence alignment is shown with positively selected sites that differ between hsMxA and agmMxA in grey (top). Dose-responsiveness of the antiviral activity of wild-type MxA and L4 chimeras was determined by co-transfecting increasing amounts of MxA expression constructs with the THOV minireplicon into 293T cells. MxA antiviral activity is measured as described in Figure 2A (middle). The Western blot analysis depicts the expression levels of the wild-type and chimeric MxA proteins in the cell lysates (bottom).
C. Restriction of THOV infectivity by human and AGM MxA is contingent on a single amino acid. Data are presented as percent THOV infected, Mx-positive cells as measured by immunofluorescence for THOV NP and MxA. Error bars represent standard deviation of three biological replicates. ***, p<0.0001 (t-test). See also Figure S2.
D. Antiviral activity of hsMxA 561 variants. Data are presented as described in Figure 2A. **, p<0.001 (t-test) for values compared to hsMxA(T103A).