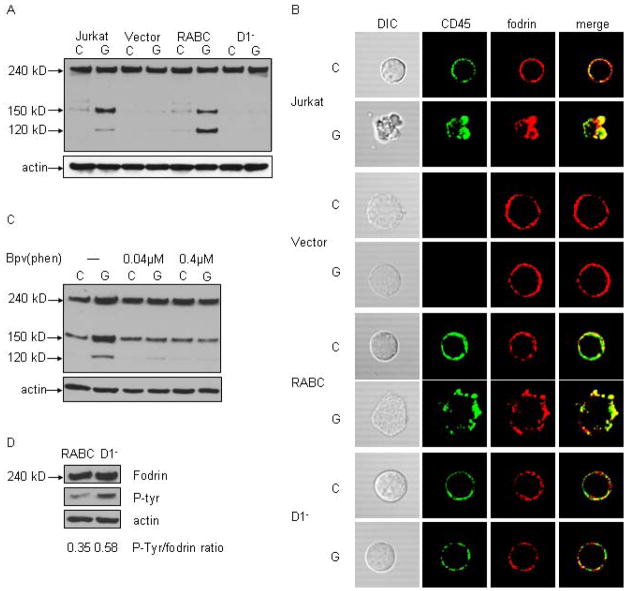
Figure 4.
Expression of CD45 is sufficient to restore fodrin cleavage after galectin-1 binding. J45.01 T cells were transfected with vector alone (Vector), full-length murine CD45(RABC) or CD45 lacking the intracellular D1 phosphatase domain (D1−). A) Fodrin cleavage was not detected in J45.01 cells transfected with vector alone. Expression of CD45RABC restored fodrin cleavage after galectin-1 binding, while no fodrin cleavage was detected in D1− cells. B) CD45 (green) and fodrin (red) localization was examined by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. Cells expressing CD45RABC demonstrated membrane blebbing, CD45 clustering and fodrin redistribution after galectin-1 treatment, comparable to that observed for Jurkat cells, while these changes were not seen in D1− cells. C) Jurkat cells were treated with indicated concentrations of the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor bpV(phen) prior to galectin-1. Inhibitor treatment abrogated fodrin degradation. D) Fodrin was precipitated from RABC and D1− cells, and immunoblots probed for phosphotyrosine and fodrin. The ratio of phosphorylated fodrin/total fodrin in RABC cells was reduced compared to D1− cells. Data are representative of three independent experiments.