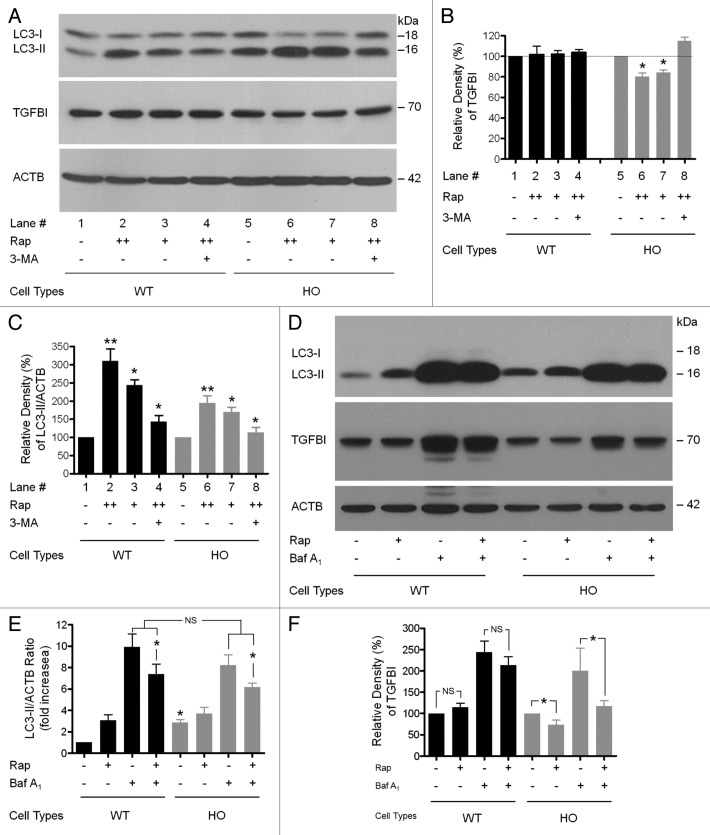
Figure 7. Rapamycin-mediated activation of autophagy enhanced the clearance of Mut-TGFBI. At 60–80% confluence, cells were treated with inhibitors for 14 h. (A) Cells were treated with either rapamycin or DMSO, and extracts were probed with anti-TGFBI and anti-LC3 antibodies. Rapamycin (Rap) decreased the levels of mut-TGFBI in HO corneal fibroblasts. Representative blots are shown of samples from three independent experiments. (B) Autophagy was measured as the ratio of LC3-II/ACTB from immunoblots shown in (A) following normalizing of protein levels to ACTB using densitometry. (C) Quantification of the TGFBI levels in (A). Baf A1 (0.1–0.2 μM) and Rap (100 nM) were added to the medium where indicated. (D) WT and GCD2 HO corneal fibroblasts were treated with Rap (100 nM) and Baf A1 (0.1 μM) individually and in combination for 14 h. Cells were lysed and immunoblotted with anti-LC3 (first panel), anti-TGFBI (second panel) or anti-ACTB (third panel) antibodies. Autophagy was measured as the ratio of LC3-II/ACTB and is represented as the fold increase in this ratio relative to WT untreated corneal fibroblasts. (E) The ratio of LC3-II/ACTB shown in (D). (F) Quantification of the TGFBI levels shown in (D). Results represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; NS, not significant.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.