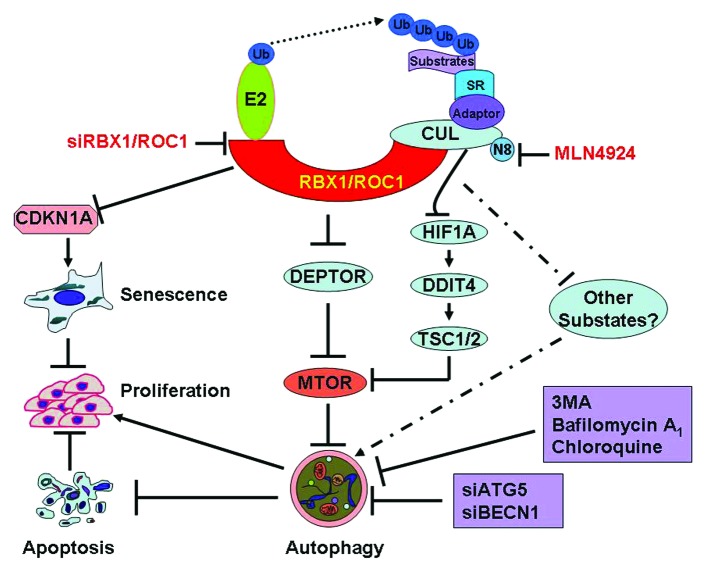
Figure 1. Inactivation of RBX1-CRL E3 ligase triggers protective autophagy. RBX1 is an essential subunit of CRL, which binds to CUL and substrate receptors to assemble functional CRLs. As an appealing anticancer target, RBX1 knockdown induces CDKN1A/p21-dependent senescence to suppress the growth of liver cancer cells. Interestingly, RBX1 knockdown also triggers an autophagy response by inducing the accumulation of the MTOR-inhibitory protein DEPTOR, resulting in the inactivation of MTOR. Similarly, CRL inhibitor MLN4924 also triggers autophagy by blockage of MTOR signals via DEPTOR as well as the HIF1A-DDIT4/REDD1-TSC1/2 axis. The autophagy response serves as a prosurvival signal since blockage of the autophagy pathway via siRNA silencing of essential autophagy genes (ATG5 or BECN1) or treatment with autophagy inhibitors significantly enhances the growth-suppressive effect of RBX1-CRL inactivation by triggering massive apoptosis in cancer cells. SR, substrate receptor, 3MA, 3-methyladenine, N8, NEDD8.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.