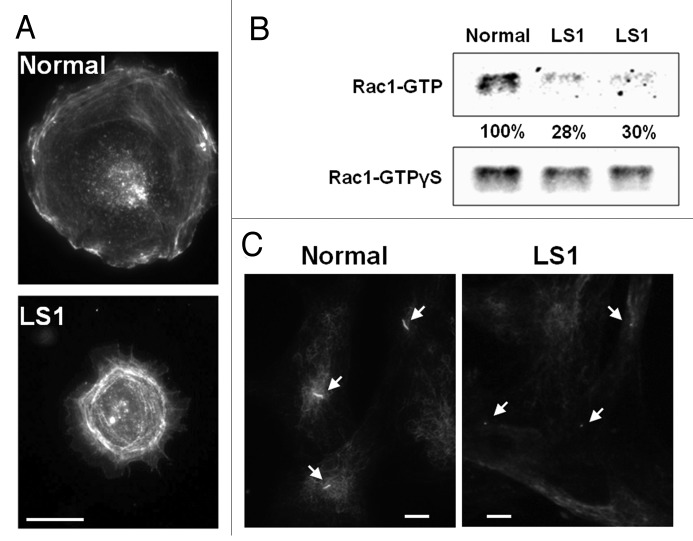
Figure 1. Cellular phenotypes of Lowe syndrome patient cells. A. Cell spreading abnormalities. Normal and LS cells were resuspended and seeded on fibronectin-coated surfaces. After 30 min, the cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde, stained with rhodamine–phalloidin and imaged. Scale bar: 20 microns. B.Rac1 activation deficiencies. Lysates from Normal and LS patient (LS1 and LS2) fibroblasts were incubated with GST-PAK1 (CRIB) beads that bind (activated) Rac1-GTP. Bound Rac1-GTP was detected by western blotting using an anti-Rac1 antibody. Results were analyzed by band densitometry. GTPγS -loaded lysates contained equivalent amounts of Rac1 in all samples. Levels of Rac1-GTP (normalized relative to corresponding GTPγS -loaded Rac1 signal) were calculated as a fraction of Normal cell values. C.Primary cilia assembly defects. Dermal fibroblasts from a normal individual and a LS patient (LS1) were grown on coverslips and induced to form primary cilia by serum-starvation. Following fixation with 4% formaldehyde the cells were immunostained using an anti-acetylated tubulin specific antibody. Arrows point to primary cilia. Scale bar: 20 microns.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.