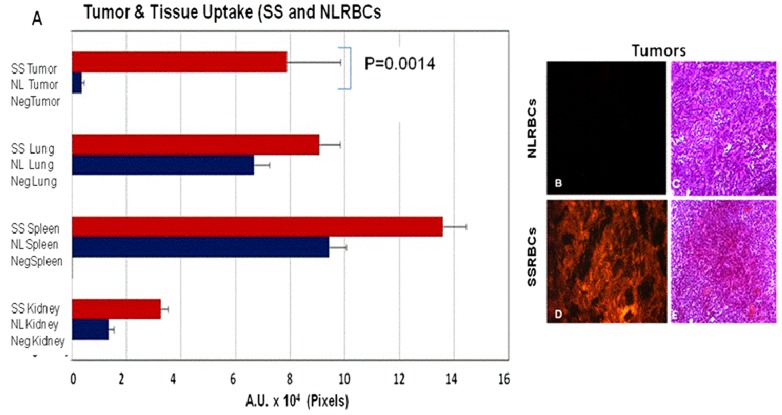
Figure 5. SSRBCs accumulate to a significantly greater degree in tumors compared to NLRBCs.
RFP-labeled SSRBCs (n = 4) or NLRBCs (n = 2) were injected into mice bearing eight day old 4T1 tumors. Twenty four hours later tumors and organs were collected and RFP fluorescence quantitated on sections of tumors and organs. The uptake of SSRBCs in tumors is significantly greater than NLRBCs (p = 0.0014) (A, B, D). In contrast, the uptake of SSRBCs and NLRBCs is not significantly different in the spleen, lungs and kidneys (p>0.05) (A) (Magnification 5×). H&E tumor sections from SSRBC-treated mouse show focal areas of cytoplasmic eosinophilia consistent with ischemia (E) not present in tumors treated with NLRBCs (C) (Magnification 20×). Abbreviations in legend: negTumor, negLung, negSpleen, negKidney mean mice injected with NLRBCs or SSRBCs without RFP label.