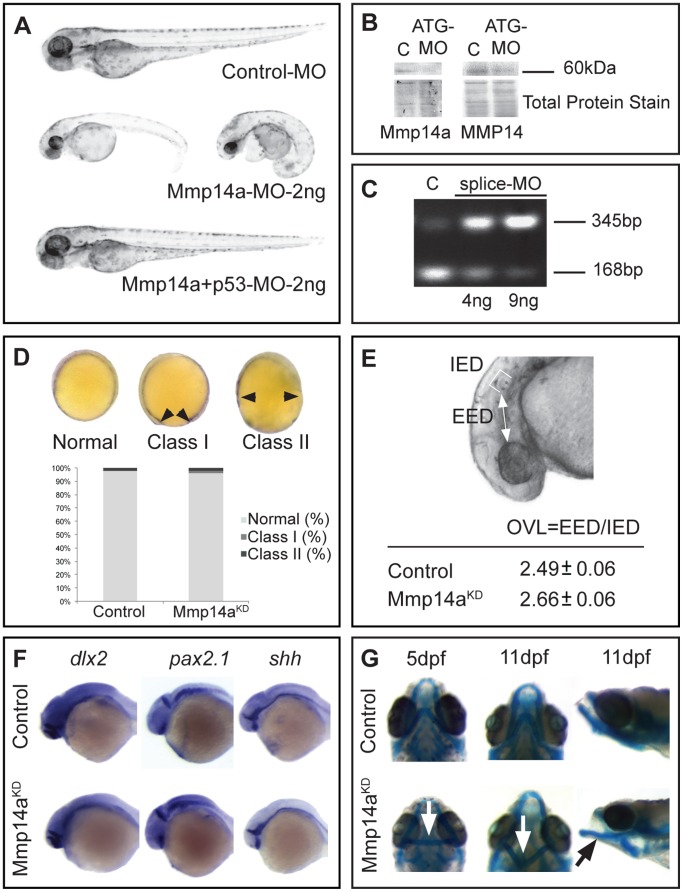
Figure 4. Mmp14a knockdown minimally affects overall embryonic morphogenesis.
A Knockdown of Mmp14a with 2 ng of Mmp14a-ATG MO at 3 dpf results in embryos with edema and a deformed body axis. However, embryos injected with 2 ng of both Mmp14a-ATG and p53 MOs do not show any morphological abnormalities. B Validation of Mmp14a-ATG MO efficiency via Western blotting using antibodies to zebrafish Mmp14a or to mouse MMP14, reveals reduced levels of active Mmp14a protein (60 kDa band) in 30 hpf Mmp14a morphants. Total protein coomassie blue staining was used for loading control. C RT-PCR analysis of Mmp14a-splice MO injected embryos reveals efficient splice blocking, resulting in a dose-dependent increase in aberrantly spliced mmp14a mRNA (345 bp band) and a concomitant decrease in correctly spliced mmp14a mRNA (168 bp band). D Semi-quantitative scoring of gastrulation defects at the tail bud stage (10 hpf) does not reveal a significant delay in gastrulation in Mmp14a morphant (Mmp14aKD) embryos, as compared to control embryos. The black arrowheads indicate the position of the germ cell layer (n = 141 from 3 independent experiments). E Measurements of the OVL, analysed by dividing EED by IED, in 31 hpf embryos, confirms the absence of a developmental delay after Mmp14a knockdown (n = 86 from 2 independent experiments). F Whole mount in situ hybridization for the neural markers dlx2, pax2.1 and shh shows normal development of the brain in control and Mmp14a morphant embryos at 32 hpf (n = 20 from 2 independent experiments). G Combined knockdown of Mmp14a and p53 (Mmp14aKD) only results in minor craniofacial abnormalities, including mild malformations of the Ceratohyal cartilage (white arrow) and the Meckel's cartilage (black arrow) at 5 and 11 dpf. Left and middle panel are ventral views, the right panel is a lateral view. C, control; dpf, days post fertilization; EED, Eye-Ear-Diameter; IED, Inner-Ear-Diameter; hpf, hours post fertilization; MO, morpholino; OVL, Otic Vesicle Length.