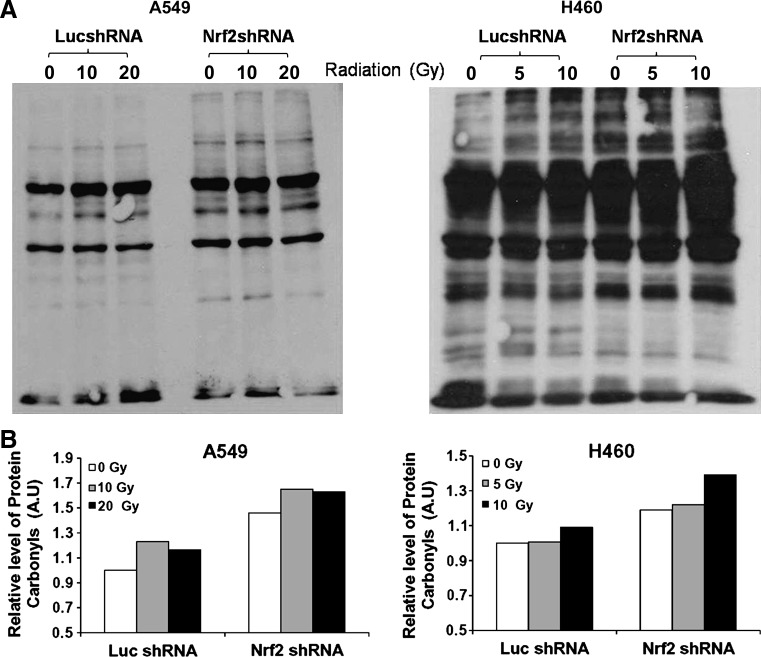
FIG. 4.
Ionizing radiation induces increased protein oxidation in Nrf2-depleted lung cancer cells. Exponentially growing A549 and H460 cells were exposed to ionizing radiation, and protein carbonyl content was analyzed 24 h post irradiation. A549 cells were exposed to a radiation dose of 0 Gy, 10 Gy, and 20 Gy. H460 cells were exposed to a dose of 0 Gy, 5 Gy, and 10 Gy. (A) Increase in protein carbonyl content in A549 Nrf2shRNA and H460-Nrf2shRNA cells in response to radiation exposure was detected by immunoblotting. (B) Densitometric quantification of relative protein carbonyls in control and radiation exposed A549 and H460 cells. The values in 0 Gy exposed Luc-shRNA cells was arbitrarily set to 1 (arbitrary units [A.U.]). Band intensities were quantified using Image-J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD).