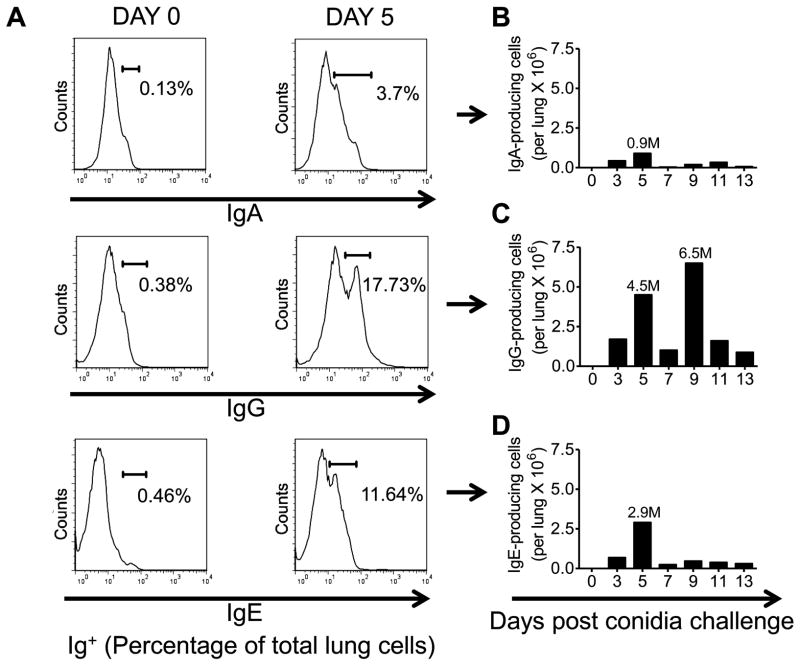
Figure 4. Effect of A. fumigatus conidia inhalation on Ab-producing cells in the allergic murine lung.
Mice were exposed to A. fumigatus according to the schedule shown in figure 1. At days 0, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13 the lungs were harvested and immediately processed into a single cell suspension. Fluorescent anti-IgE, IgG and IgA antibodies were used to identify antibody producing cells. (A) Histograms representing the total percentage of Ig+ (IgA/IgG/IgE) cells in the lungs of day 0 (sensitized, unchallenged with A. fumigatus) and day 5 BALB/c mice. (B) Total number of IgA+ cells in the lungs of day 0 and day 5 (sensitized and challenged with A. fumigatus) BALB/c mice. (C) Total number of IgG+ cells in the lungs of day 0 and day 5 (sensitized and challenged with A. fumigatus) BALB/c mice. (D) Total number of IgE+ cells in the lungs of day 0 and day 5 BALB/c mice. n=4–5 mice/group and all the lung sections were pooled together for antibody staining.